8 Radical Advances in the Evolutionary Battle between Science & Pathogens - Special Feature
Discover the cutting-edge ways science and technology are taking on infectious diseases to help make the future healthier
30 Apr 2018
A century ago, infectious diseases were among the most frequent causes of death worldwide. By 1928, penicillin was discovered, and by the 1950s, the antibiotic compendium was increasing exponentially. Yet with the golden era of antimicrobials quickly came the age of multi-drug resistant bacteria, not to mention the emergence of deadly new viral pathogens. But science is catching up fast, and in this special feature we highlight just a few of the scientists leading the world's evolutionary arms race. Find out how researchers are fighting antimicrobial resistance with smart phone technology, battling to find a cure for HIV and unlocking the science behind bacterial ‘communication’. Plus, listen to a Clostridium difficile infection prevention masterclass and find out why the new EM smart reader by ELITech is making waves in the field of microbiological automation.
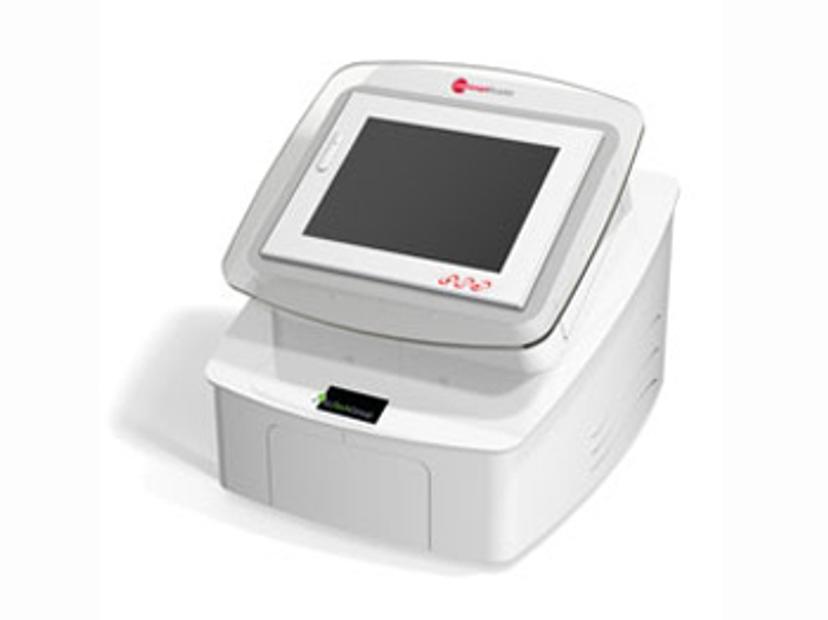

1. Innovative Technology to Accelerate Mycoplasma Diagnoses
Finding a fast, simple and cost-effective method for identifying microbial specimens in patient samples is essential to successful patient care. With ELITech Group's latest innovation, the EM SmartReaderTM, healthcare professionals can automatically confirm the diagnoses of urogenital mycoplasma infections from a variety of clinical specimens. Learn how this device enables hands-free patient sample analysis and reporting on a compact and intuitive touchscreen platform.

2. Combating Antimicrobial Resistance with Smart Phone Technology
Scientists from the University of Southampton are developing a solution to antimicrobial resistance in the form of digital microfluidics. Using the same technology embedded in mobile phone displays, they can control up to 17,000 droplets, each performing unique isothermal RPA (recombinase polymerase amplification) reactions to pinpoint key resistance genes. With this, they aim to produce a rapid diagnostic kit for identification of multi-drug resistant populations in patient samples. Check out the video to learn how this revolutionary diagnostic tool could accelerate precision medicine in the field of clinical microbiology.
3. Copper Coated Uniforms to Fight E. Coli Outbreaks in Hospitals
Did you know that some metals have excellent antibacterial and antimicrobial properties? Learn how researchers at the University of Manchester, in collaboration with universities in China, have developed a material coated with copper nanoparticles via ‘polymer surface grafting’ to help prevent the spread of infection in hospitals. Hospital acquired infections are a major issue in healthcare — E. coli infections alone were responsible for more than 5,500 deaths in the UK in 2015.
4. How Do Bacteria Communicate?
When we think of electrophysiology, we think of neurons and the brain. But Dr. Suel reveals in this compelling webinar that this kind of cell-to-cell communication is in fact used by bacterial biofilms, in order to coordinate population level behaviors. Fascinatingly, these can include changes in metabolic state and protein expression. Find out more and observe biofilm electrophysiology in real time by watching our webinar on demand.
5. Finding Better Vaccines for Filoviruses
Filoviruses are a group of viruses endemic to central and western parts of Africa, associated with haemorrhagic fever and shock, and often result in death. In this interview, Lizzie Clarke, Ph.D. student at the University of New Mexico, shares her lab’s work on filovirus as they strive to develop a better vaccine. One of their key projects involves researching the non-infectious, non-replicating virus-like particles (VLPs) as a novel vaccine platform. VLPs are made from proteins that comprise the outer shell of a virus, resembling live viruses in vivo. Visit The Scientists’ Channel to discover more.

6. Future Steps for Preventing the Antimicrobial Apocalypse
The AMR center, based in the UK, focuses its efforts on tackling the growing antimicrobial resistance concern. Key projects include the development of antimicrobial peptides for extremely drug resistant specimens, and the metallobetalactamase inhibitor (MBLI) program. Discover more in this SelectScience interview with Dr. Peter Jackson, executive director of the AMR Centre.

7. Clostridium Difficile: An Infection Prevention Masterclass
Rapid diagnosis and treatment of Clostridium difficile infections is vital to prevent spread and reduce patient mortality. Furthermore, clinical laboratories play an essential role in implementing preventative measures. Watch this SelectScience webinar to hear associate professor of medicine, Dr. Erik R. Dubberke, deliver a masterclass on existing diagnostic assays and how to avoid future Clostridium difficile infections.
8. Advances in Mission to Find HIV Cure
Since the discovery of the HIV virus in the 1980s, medicine has advanced tremendously, and patients are now able to lead relatively healthy and normal lives. The quest for a cure continues, however, as advanced immunoassay technology, including the Quanterix Simoa HD-1, is enabling researchers to detect and quantify ultra-trace level HIV proteins. With this information we are able to better understand the virus’ biology, as well as detect cells capable of harboring and propagating the pro-virus. In this interview with Bonnie Howell, executive director in the department of infectious disease and vaccines at Merck, discover how close scientists are to finding an HIV cure.
