Cancer Pathway Compendium: Downloadable Content for Your Lab
Receive your 4 free cancer pathway posters for MAPK, NF-ƘB, WNT and JAK/STAT, to help you select the best antibodies and small molecules for your cancer research assays
12 Nov 2018
With an extensive range of carefully validated small molecules and antibodies for life sciences and pre-clinical research, scientific experts from Biorbyt have put together a collection of prominent signaling pathways to help you choose the best for your applications. The devil is in the detail when it comes to analyzing the complex cancer proteome. This article presents recent updates in the field, with links to your free pathway downloads.
Advances in technology over the past decade have unlocked many of the molecular secrets of cancer: frequently-mutated pathways are well documented and common driver vs. passenger mutations continue to be identified. In one of the most comprehensive studies of cancer genetics, published in Cell Press earlier this year, researchers found approximately 300 unique genes to be actively driving tumorigenesis. Such findings have enabled the field to make great strides in developing new treatment strategies that target patient-specific transformations.
A recent review of 33 cancer types, in more than 10,000 tumor samples, evaluated 10 canonical signaling pathways, including MAPK, TGFB, PI3K/AKT, p53, and Wnt, among others. The RTK-RAS-MAPK pathways had the highest median frequency of alterations – mutated in 46% of all samples. KRAS was the most frequently altered gene across the entire population. The same study also discovered the emergence of mutational co-occurrences in certain tumors, and this was more prominent in the Wnt, Hippo, and MAPK pathways.
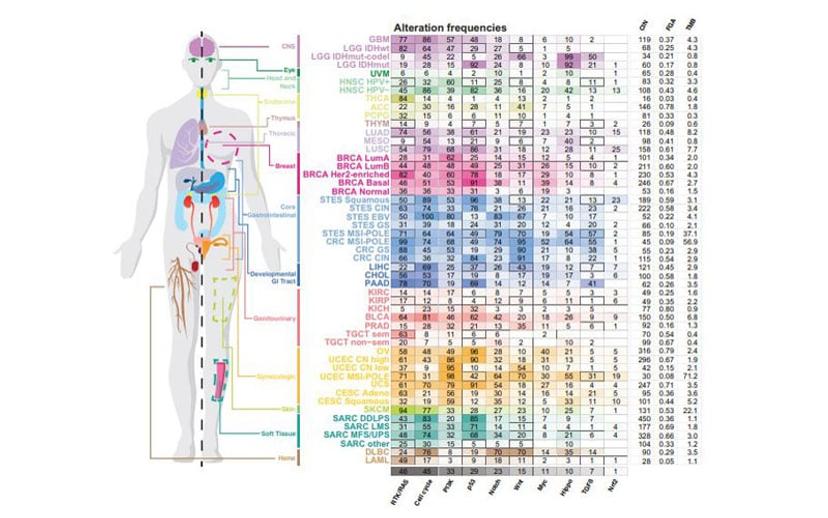
Evidently, cancer is a remarkably heterogeneous disease where complex protein interactions, post-translational modifications and cross-talk between signaling axes, all occur. There should be careful consideration of these, therefore, when selecting the most suitable antigens and antibodies for your molecular investigations. Download the pdfs below to refresh or update your knowledge.
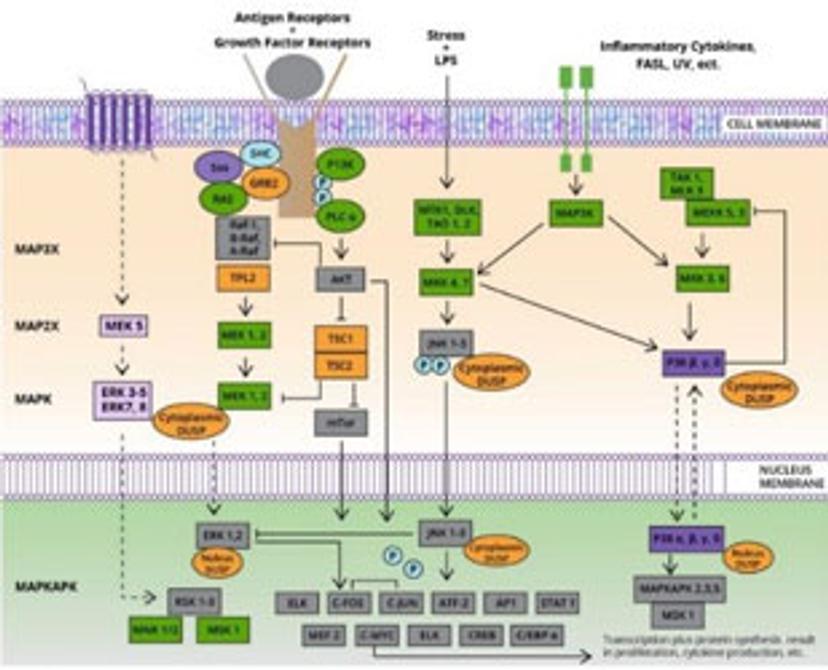
MAPK
One of the most commonly hyper-activated pathways in cancer, the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway comprises a super-family of kinase enzymes activated by a diverse range of extracellular stimuli. Progress in the targeting of this pathway has been hindered by the emergence of resistance mechanisms, but recent success has emerged with drug candidates targeting key protein interactions. Signal transduction occurs by sequential phosphorylation of pathway components that go on to activate transcription factors involved in promoting survival, proliferation, differentiation, and death.
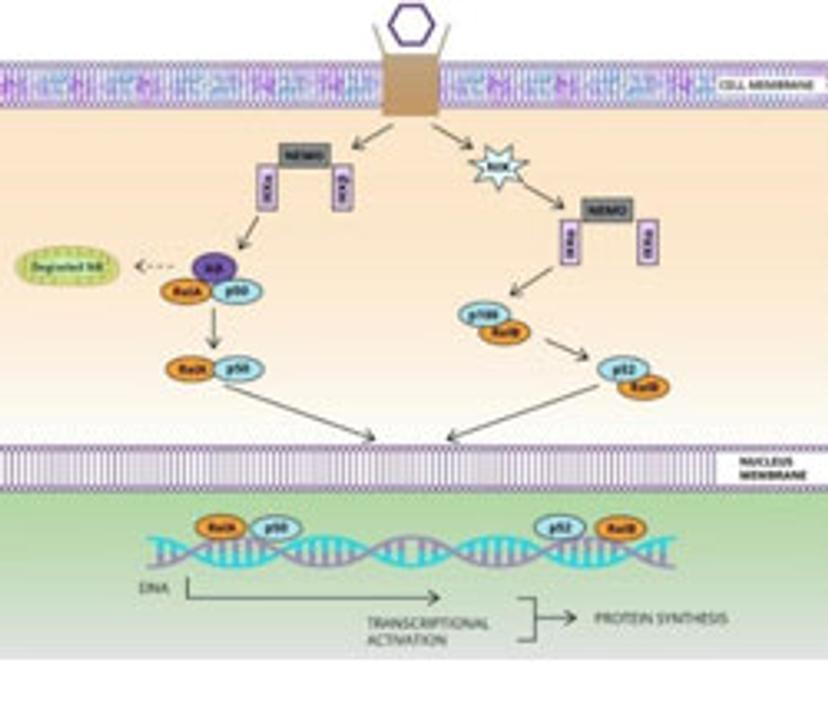
NF-ƘB
A crucial regulator of immune response, both innate and adaptive, NF-kB plays a significant role in cancer; overexpression is particularly characteristic of lymphomas and leukemias, but also plays a role in mammary biology and gastric adenocarcinoma development. With the recent upsurge in immunotherapy research, NF-kB signaling has recaptured the attention of the field – believed to mediate resistance mechanisms in CAR-T or checkpoint inhibitor therapy, as well as promoting invasion, angiogenesis and metastases. Given its dual role in immune biology, promoting both pro- and anti-inflammatory mechanisms, future perspectives involve targeting NF-kB regulators. One recent study demonstrated that inhibition of the associated protein, Rel, potentiates anti-PDL1 therapy, since its function is crucial for T-reg cell immune checkpoints.
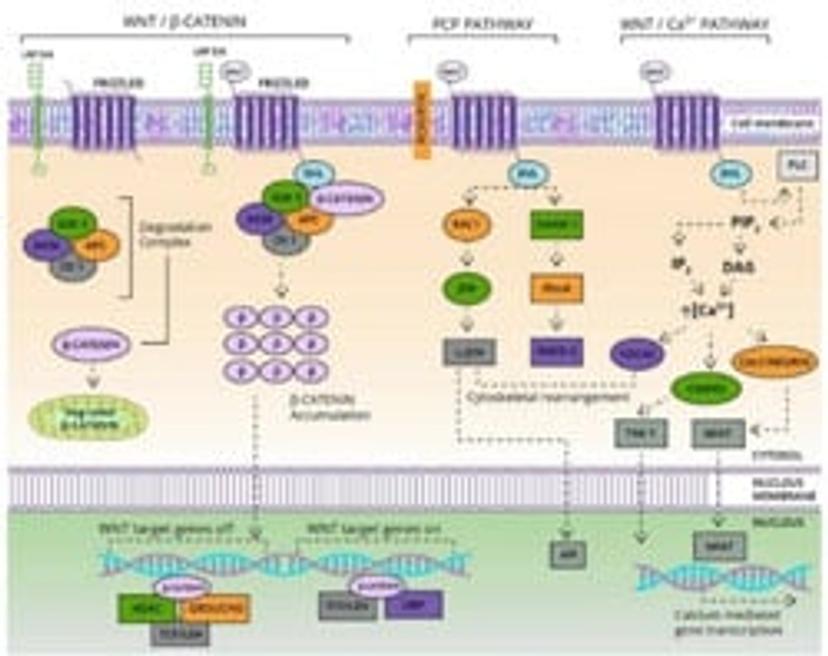
WNT
A family of secreted glycolipids, the Wnt proteins play a considerable role in cell differentiation, growth, and proliferation from one of three well-studied pathways: the beta-catenin canonical, planar and calcium pathways. Research has shown that Wnt proteins are involved in the activity of cancer stem cells, which corresponds with their known involvement in cellular plasticity and self-renewal. Wnt proteins transduce signals through LGR5, and this is a representative cell-surface marker of CSCs. There is also evidence to suggest Wnt proteins are involved in modulating the anti-cancer immune response. Therapeutic modulators of the Wnt pathways may therefore prove efficacious in combination with immunotherapies in the near future.
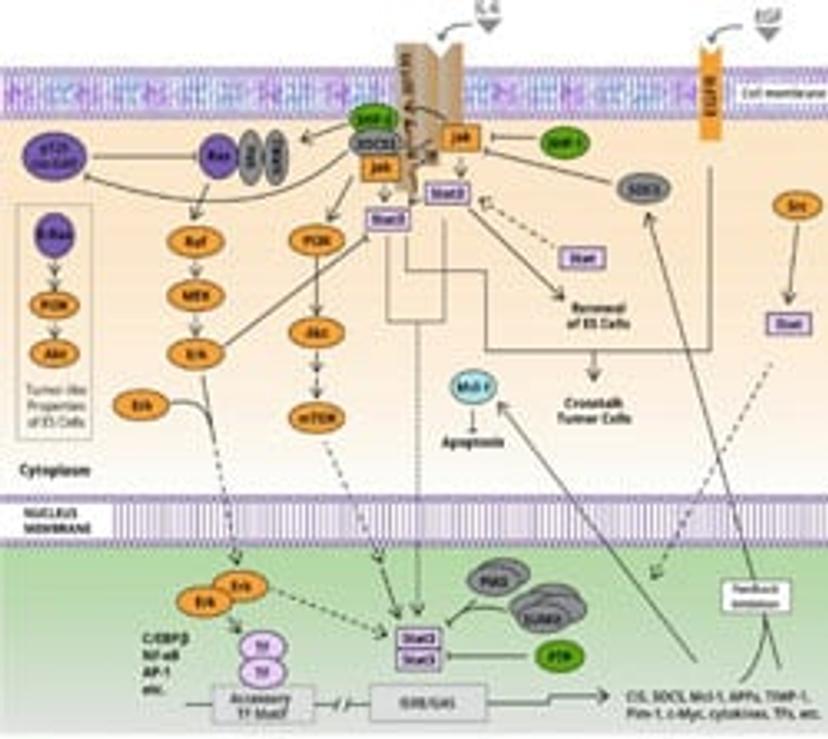
JAK/STAT
JAK/STAT signaling drives several key homeostatic and developmental processes in the cell and is activated by cytokine stimulation, or growth factor activation, of multiple receptor types, including G protein coupled receptors or growth factor receptors. Its wide variety of activators make it a unique kinase. The phosphorylation of JAK activates STAT proteins, as well as PI3K, MAPK and TGFB signaling pathways. STAT proteins, of which seven exist in total, are both second messengers and transcription factors, capable of altering the expression of genes involved in the survival of cancer cells. In 2013, the JAK/STAT axis was deemed as one of the core cancer pathways, and several studies have implicated IL-6/gp130/JASK2/STAT3 in triple negative breast cancer development.
Browse Biorbyt’s range of antibodies >>
References:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?Db=pubmed&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=23539594
http://mct.aacrjournals.org/content/17/1_Supplement/B087
https://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/ijo.2017.4129?text=abstract
https://www.cell.com/cell/pdf/S0092-8674(18)30359-3.pdf