Complete Solutions & Information Resources for Environmental Trace Metal Analysis
Find environmental metal analysis application notes, blogs, articles and webinars at Thermo Fisher Scientific
13 Dec 2016

Image: Shutterstock/Ruengwit
Editorial Review by Lois Manton O’Byrne, Editor, SelectScience®
Drinking water, wastewater, solid waste, soils and compost are all commonly tested for environmental metals. Different metals have unique properties and different methods of sample preparation, ionization and spectral interferences.
Different instruments are required for different environmental applications, this is dependent on variabilities such as sample throughput, matrices and regulation requirements. Read this blog post on trace elemental analysis to discover which instrument is best for your requirements. Written by Dr. Maura Rury, Trace Elemental Analysis, this article discusses regulatory requirements, how to choose the best technique for your applications, as well as factors to consider when choosing an instrument.
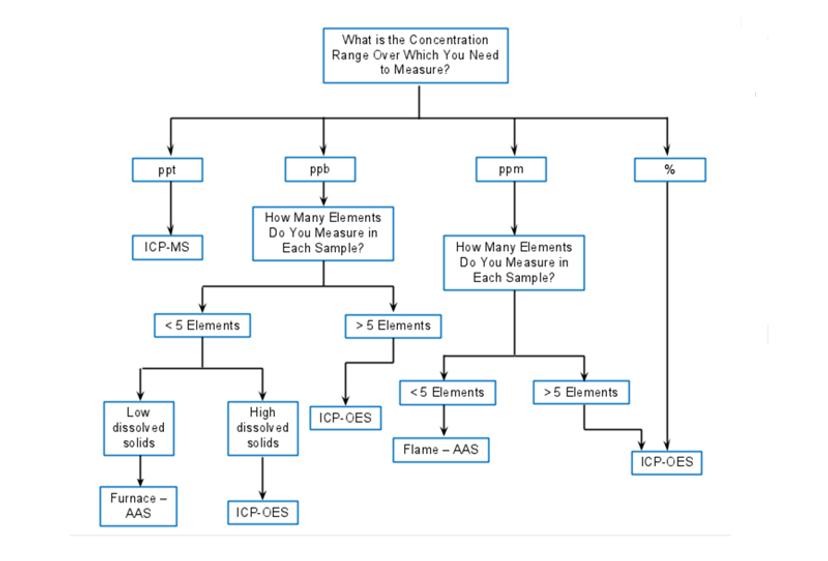
Figure 1: Flow chart to help guide product selection, from Part 1: Trace Elemental Analysis: Which Instrument is Best for You1
Sample preparation for metal analysis can be carried out on solid matrices, however most samples are analyzed in liquid form. Rapid and consistent sample preparation is a key requirement for producing good data quality and fast turnaround times. Learn more about sample preparation for trace metal analysis in this free webinar with Dr Daniel Kutscher and Sanja Asendorf, Thermo Fisher Scientific.
Improving metal analysis productivity is extremely important when analyzing large numbers of samples in big laboratories. The Thermo Fisher Scientific Trace Metal Analysis webpage contains numerous resources to help you to improve productivity. Download this application note to find out how the Thermo Scientific™ iCAP™ 7000 Plus Series ICP-OES maintains long term analytical stability to save on operational costs.
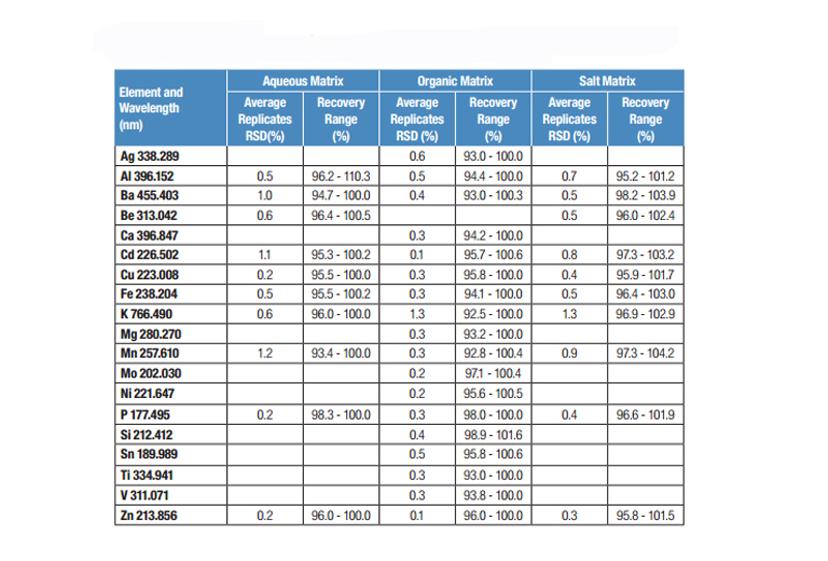
Figure 2: Average RSDs of replicates and recovery range for stated element wavelengths in %2
You can also read a series of blog posts entitled ‘Your Elemental Analysis is Costing You More Than You Think’. These informative articles discuss ways in which a laboratory can maximize productivity and improve profitability.
Discover how to further maximize productivity byimproving matrix tolerance, by reading these application notes on analysis of high matrix samples using argon gas dilution, and automated sample preparation with the Thermo Scientific™ iCAP™ Q ICP-MS .
Nanoparticles analysis using ICP-MS has also been of increasing interest to environmental scientists in the last few years. With the emergence of nanotechnology in the early 1980s, an increasing number of so-called engineered nanomaterials have been created. Nanoparticles are used today in a variety of applications including medical, cosmetic, environmental and energy fields. As a proportion of these particles end up in our water supplies and food, there have been increasing concerns about their possible toxicity. Read this fascinating blog, Nanoparticles: A Storm in a Teacup or Something to Worry About, to learn about nanoparticle analysis using ICP-MS.
Visit the Thermo Fisher Scientific Metal Analysis page for more webinars, blog posts and technical notes.
References:
Blog Post: Trace Elemental Analysis: Which Instrument is Best for You?
Application Note: Highly stable performance of the Thermo Scientific iCAP 7000 Plus Series ICP-OES Radial for aqueous, organic and high dissolved solids sample matrices
