Eight important ways connected-worker technology enhances efficiency in laboratories
Eric Whitley, Director of Smart Manufacturing at L2L, shares how adopting connected worker technology is key for true digital transformation of your lab
8 Oct 2023
From the evolution of traditional workflows to the role of AI, cloud computing, and data programming, the landscape of lab work is undergoing a significant transformation – and it is happening under the umbrella of connected-worker technology.
Adopting connected-worker technology is not just a trend but a necessity for labs aiming to stay competitive and efficient. Embracing these technologies can lead to faster research outcomes, improved data integrity, and ultimately, a more streamlined and effective laboratory environment.
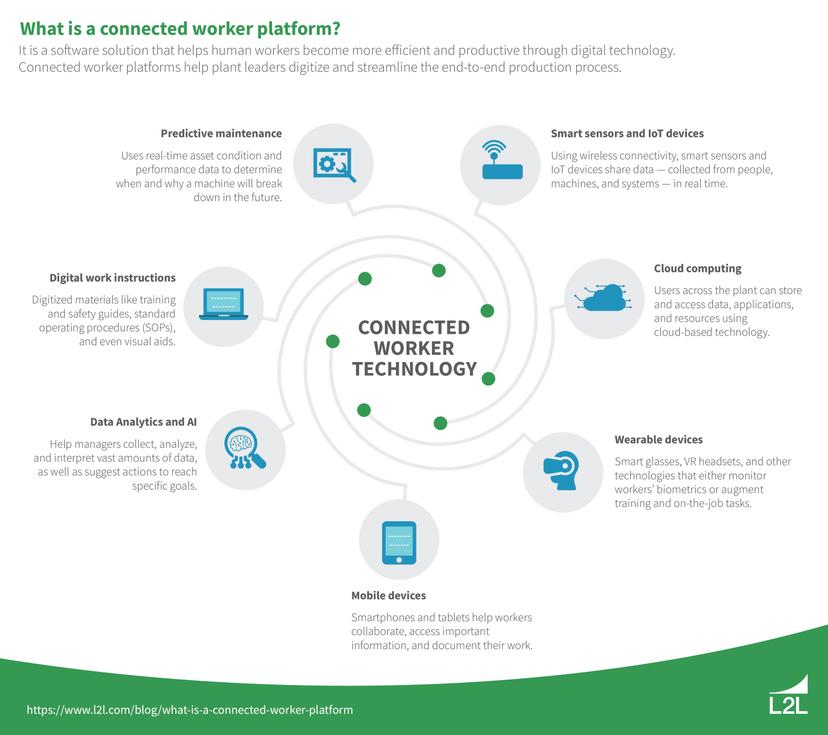
Connected-worker technology is the integration of digital tools and platforms that enable seamless communication, data sharing, and real-time monitoring among lab personnel. These technologies range from electronic notebooks and wearable devices to specialized software that facilitate better workflow management.
Efficiency in laboratories is paramount for several reasons, including the timely delivery of research results, an optimal use of resources, and an assurance of high-quality outcomes. In this guest editorial article, explore how connected-worker technology can make laboratories significantly more efficient and revolutionize the way scientists work.
Evolution of laboratory workflows
Labs used to be dominated by tedious manual processes – manual data entry, indecipherable handwritten notes, and inefficient standalone instruments – which often lead to bottlenecks. Connected-worker technology can ease these bottlenecks and automate manual processes by enabling real-time communication and data sharing among team members.
Integrating digital tools into existing systems has revolutionized data acquisition, processing, and sharing. Connected-worker technology further amplifies these benefits by facilitating remote monitoring and control of these digital tools. If you have yet to embark on this journey, consider starting with an audit of your current processes and identifying areas ripe for digital intervention.
Importance of data integrity and management
Any seasoned scientist knows the ramifications of compromised data, from having to redo experiments to risking the credibility of the lab and its findings. Data integrity goes beyond just accuracy. You need to ensure that data remains unaltered and retrievable throughout its lifecycle. Connected-worker technology enables authorized personnel to access and edit data through secure, cloud-based platforms, thereby supporting data integrity.
With the influx of big data in labs, traditional data management methods are no longer viable. Advanced data analysis tools, integrated within a connected-worker technology framework, can drastically reduce data processing times, provide clearer analysis, and improve our understanding of the data. Regularly updating these tools and training staff to use them effectively is crucial for data integrity.
Potential of AI and ML
AI’s potential in labs is vast. Companies can use connected-worker technology as an interface to deploy and manage AI algorithms, which makes it easier to integrate AI into existing workflows. AI can handle tasks that were previously deemed too complex or time-consuming, like predictive modeling or image analysis; for example, in spectroscopy data interpretation or in predicting protein structures.
One notable example is the use of AI in drug repurposing. Connected-worker technology allows for the seamless integration of AI algorithms into the lab’s data ecosystem, enabling more efficient and collaborative research efforts.
By analyzing vast datasets, AI algorithms can identify new uses for existing drugs, reducing the time and cost of drug development. Another example is the use of machine learning (ML) in genomics to identify patterns and anomalies in DNA sequences, paving the way for personalized medicine.
The cloud as a facilitator
The cloud has revolutionized how we store and access data. Connected-worker technology enhances this by providing a unified platform where cloud resources can be managed and monitored in real time. No longer confined to physical servers, labs can now access data from anywhere, facilitating collaborations across continents.
Laboratory information management systems (LIMS), when integrated with cloud computing and connected worker technology, become a powerful tool. Data can be accessed remotely, and updates can be rolled out without disrupting lab operations. If your LIMS isn’t cloud-integrated yet, it’s time for an upgrade.
Technology enablers, from ELNs to TLA
Electronic laboratory notebooks (ELNs) are to traditional lab notebooks what smartphones are to rotary phones. Connected-worker technology complements ELNs by enabling real-time notifications and updates, making it easier to collaborate on ongoing experiments. They’re much more than just digital versions of paper notebooks — they offer functionalities like data linking, advanced search, and integration with other lab systems.
Beyond just data recording, ELNs, when used within a connected worker technology framework, facilitate real-time collaboration. Multiple scientists can annotate, review, and validate data simultaneously. With features like version control, audit trails, and electronic signatures, ELNs ensure data integrity and compliance with regulatory standards.
Another tech enabler is total laboratory automation (TLA), which covers everything from automating individual processes to ensuring that these processes are interconnected and optimized, making it the pinnacle of lab automation. Connected-worker technology serves as the glue that binds these automated processes together, allowing for centralized control and monitoring. TLA ensures consistency, reduces human error, and increases throughput.
Within the framework of TLA, specialized technologies like digital morphology and digital slide staining play pivotal roles in enhancing diagnostic accuracy, streamlining workflows, and reducing the time needed for specimen analysis. Connected-worker technology enables remote monitoring and calibration of these specialized technologies, ensuring their optimal performance. These technologies, while advanced, require regular calibration and quality checks to ensure accuracy.
Evolved digital pathology
Digital pathology has evolved well beyond just digitizing slides. With the integration of AI, image analysis has reached new heights. Connected-worker technology allows for the real-time sharing and analysis of these digital slides, facilitating collaborative diagnoses. Features like pattern recognition and anomaly detection allow pathologists to make more accurate diagnoses in a fraction of the time.
Consider the diagnosis of rare cancers. With digital pathology and connected-worker technology, slides can be shared with experts worldwide, ensuring that the patient receives the most informed diagnosis. Additionally, ML models can be trained on vast datasets to identify subtle patterns that the human eye might miss.
How data programming helps
Data programming allows labs to tailor workflows to their specific needs. Connected-worker technology can facilitate this customization by providing a platform for deploying custom scripts and algorithms and sharing them across the lab. Whether it is automating data-cleaning processes or developing algorithms for specialized analyses, programming provides the flexibility that off-the-shelf software often lacks.
Python, with its extensive libraries, has emerged as a favorite in many labs. However, languages like R, especially for statistical analysis, and MATLAB, for numerical computing, also have their niches. Regular training sessions and workshops, coordinated through a connected worker platform, can ensure your team stays updated with the latest tools and best practices.

For more than 30 years, Eric Whitley has been a leader in the manufacturing space. He has written on various manufacturing topics, and his work has included leading the Total Productive Maintenance effort at Autoliv ASP, along with involvement in the Management Certification programs at The Ohio State University, where he served as an adjunct faculty member.
