Latest Advances in Infectious Disease Diagnostics: SelectScience Special Feature
From rare pathogens to pandemic prevention, explore the latest techniques and technologies that are shaping today’s diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases
26 Jun 2019

Infectious diseases represent a global burden and there is an unmet clinical need for earlier and more rapid diagnostics that can prevent the progression of these diseases. Moreover, there is a need for more accurate identification of the right type of drug to administer to an infected individual, to prevent the emergence of multi-drug resistant species. In this special feature, discover which tools, technologies, and research are helping to build momentum in the battle against infectious diseases.
Microscopic Examination of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
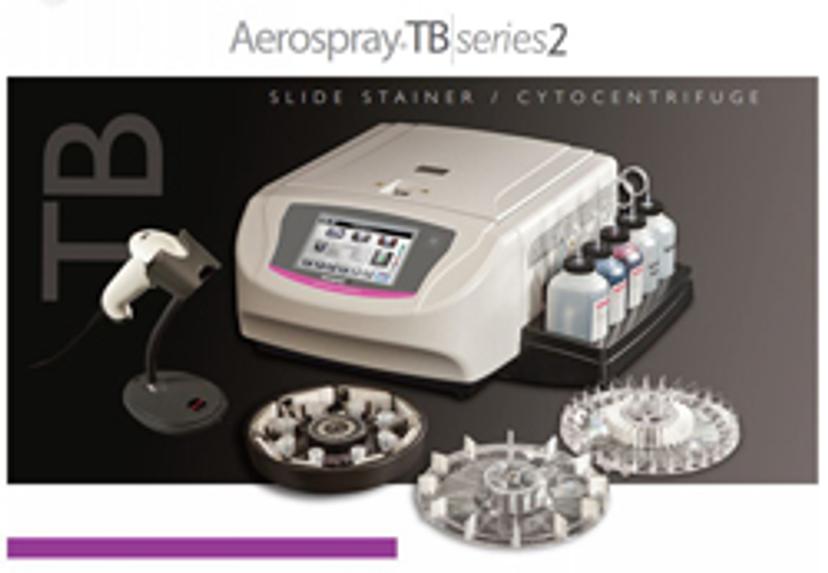
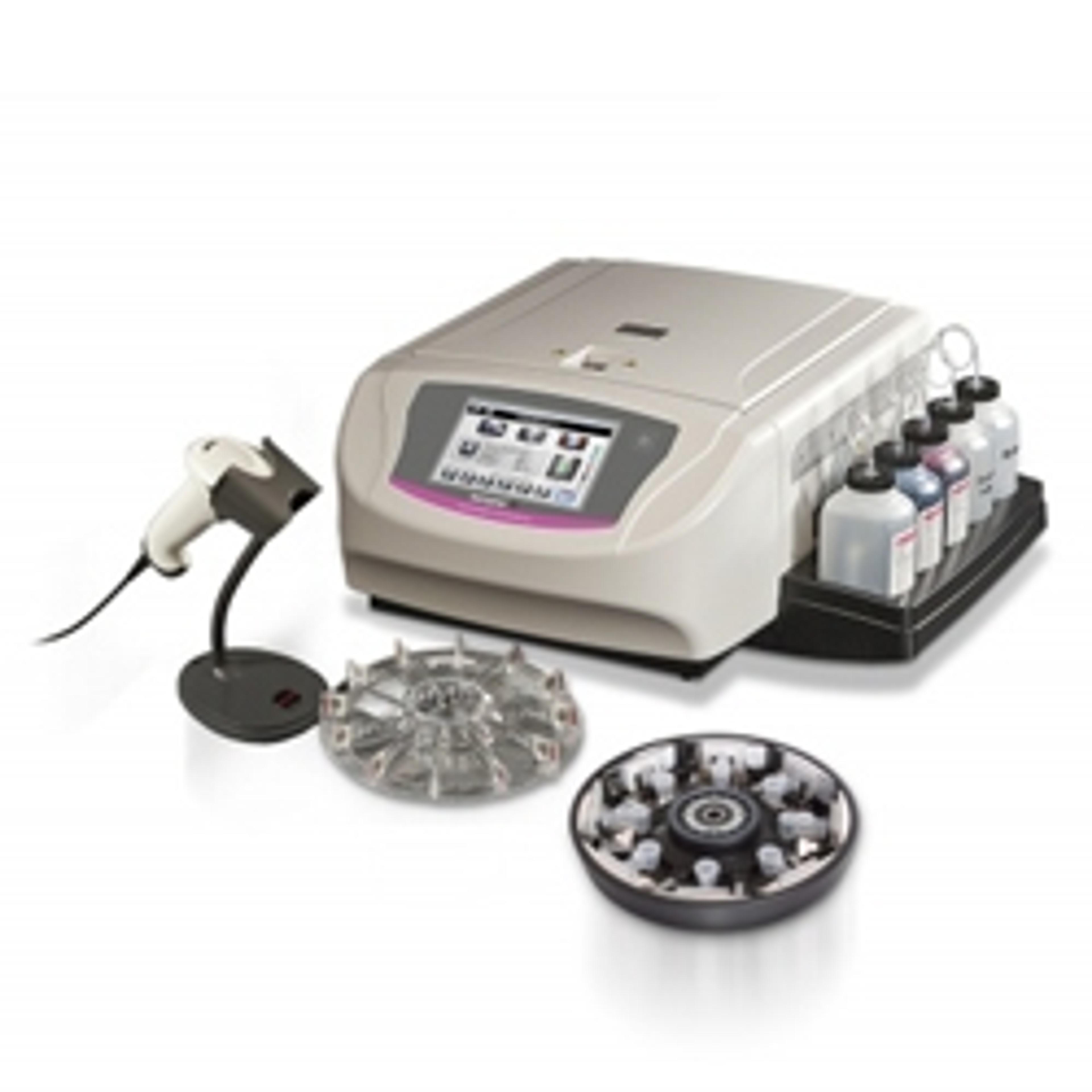
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection that is both curable and preventable with the correct vaccinations and treatment of antibiotics. Despite this, TB is one of the top ten causes of death worldwide.
Microscopic examination of acid-fast bacilli (AFB) stained smears is one of the first, easiest, cheapest, and fastest methods for demonstrating the presence of mycobacteria in clinical specimens and cultures. The Aerospray TB Series 2 Slide Stainer by ELITechGroup automates the staining routine, without the risk of cross-contamination. Three laboratories recently evaluated the Aerospray TB Series 2, comparing the system to manual staining methods, with the aim of streamlining their TB diagnostic workflows.
Early Intervention for Vector-Borne and Tropical Diseases
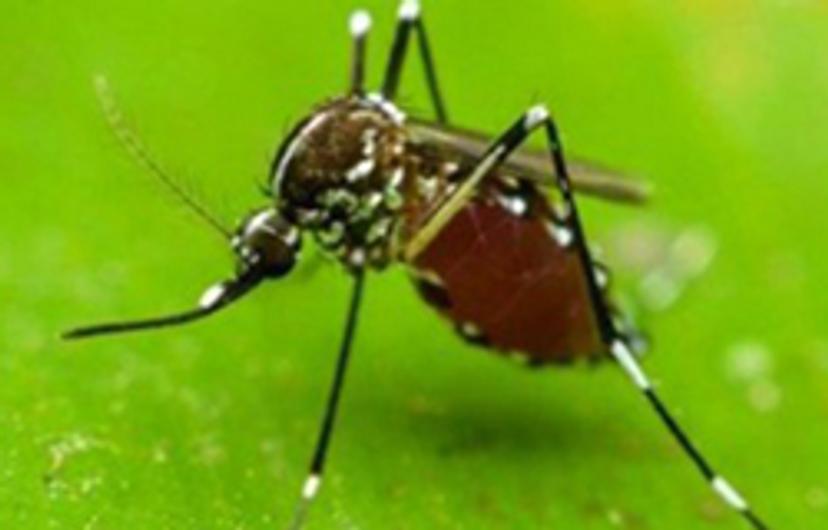

Vector-borne diseases, such as dengue and yellow fever, account for more than 17% of all infectious diseases and cause over 700,000 deaths annually. They are often prevalent in the poorest and most hard-to-reach regions of the world, making outbreaks very difficult to treat and control. Therefore, there is a need for low-cost and sensitive diagnostic methods that have little cross-reactivity to other diseases.
To aid the early diagnosis, and therefore effective treatment of these diseases, Biorbyt has developed a range of validated, matched antibody pairs that are designed fro the development of your own immunoassays and to identify potential targets, such as the NS1 protein, for use in early diagnostic tests.
Quickly Identify Rare Pathogens
Diagnosis of rare pathogens can be laborious and time-consuming due to the diversity of bacteria that can cause infection. The combination of ribosomal RNA gene amplification and sequencing analysis is a frequently used method for pathogen identification. However, contamination of reagents with microbial DNA and large volumes of human DNA negatively impact test sensitivity and specificity.
To address this, Molzym has developed a range of contamination-free kits and reagents. This method incorporates 16S rDNA PCR and sequencing analysis to deliver precise strain identification within hours, with the aim of supporting the development and adjustment of tailored antibiotic regimens for patients with critical conditions.
RNA In Situ Hybridization Assays for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
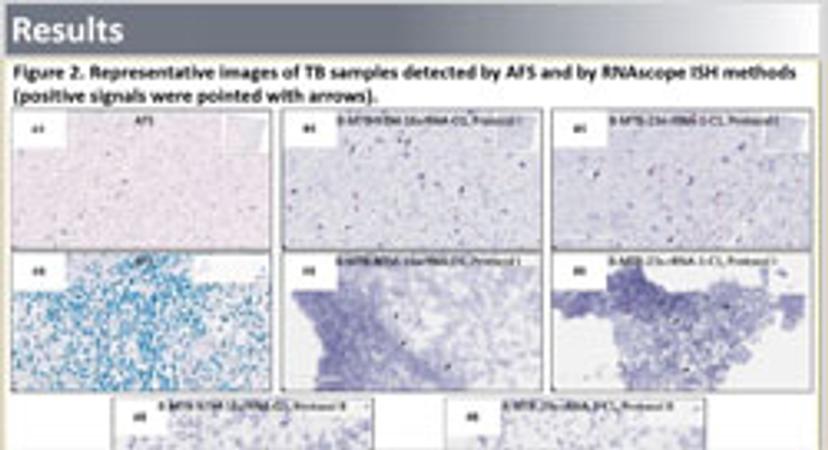
Acid-fast staining (AFS) provides a rapid method for detecting and identifying mycobacteria in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue. While a swift and straightforward method, the results can be difficult to interpret and standard tissue sample preparation can alter acid-fast organisms’ structures, reducing test sensitivity. Additionally, AFS does not currently allow for discrimination between different acid-fast organisms.
Advanced Cell Diagnostics has developed a highly sensitive and specific RNA in situ hybridization (RISH) assay, using its RNAscope technology, in order to address this issue. This method is designed to detect mycobacteria rRNA in FFPE tissues as well as distinguish between mycobacteria tuberculosis (MTB) or nontuberculosis mycobacteria (NTM).
Revolutionary Early Sepsis Biomarker
Sepsis is a leading cause of hospital mortality and without early and effective management it can lead to septic shock, organ failure, and death. Clinicians are facing several challenges in recognizing and treating sepsis quickly and, currently, there is an unmet need for rapid diagnostic tests to rule out infection and prevent sepsis progression.
Beckman Coulter’s new Early Sepsis Indicator is a first-of-its-kind, hematologic biomarker that is automatically reported as part of a routine complete blood count. Compared to reviewing the white blood cell count alone, the Early Sepsis Indicator is designed to enable physicians to initiate lifesaving treatments more rapidly.
More Hot Topics in Infectious Disease Diagnostics:
- Automation in Routine Molecular Pathogen Testing
Manual cultivation methods in routine pathogen testing regimens are both error-prone and time-consuming. A new kit developed by Molzym, the Micro-DxTM , enables rapid, automated in vitro diagnosis of microbial pathogens without the need for cultivation - minimizing the occurance of false findings. Find out the how the kit performed in this multi-center clinical evaluation study >>
- Protective Antibody Treatments for Pandemic Prevention
The Vanderbilt Vaccine Center is working to identify antibodies for use as potential complements to vaccines and develop effective medical countermeasures to deal with newly emerging infectious diseases as quickly as possible. Find out more about the project and the Sony SH800 cell sorter>>
- Rapid HbA1c Test for Diabetes Diagnosis
The first ever point-of-care glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) test, the Afinion™ HbA1c Dx assay, promises accurate and precise results in just three minutes, allowing clinicians to develop individualized management plans during a patient visit. Find out how Abbott is hoping to set the standard for diabetes diagnostics>>
- Multiplexed Immunogenicity Screening Assays
Facilitated by the use of Luminex’s xMAP® Technology, the development of multiplexed FLAVI screening assays promises to provide a broad picture of patient status before the administration of a vaccine. Listen to Eric Shaw, of Takeda Vaccines, discuss how this development is set to advance flavivirus vaccination research>>
Related Resources
Webinars:
Automating Urinalysis at the Point of Care
Improving the Quality and Management of Your Point-of-Care Testing Environment
How-to-buy guides:
Hematology Analyzers and Stainers
Videos:
Infections and Cancer - Understanding Changing Trends in the Population with Multiplex Serology
Taking Steps Towards Discriminating all Pneumococcal Serotypes with Multiplex Serology
Explore Scientific Innovation on The Scientists’ Channel
Discover leading scientists on video:
- Dr. Prakasha Kempaiah – Advances in Malaria Research: Host Genetic Factors and Overcoming Drug-Resistant Antimalarials
- Lizzie Clarke – Our Quest for a Better Vaccine to Combat Filovirus Outbreaks




