Nucleic acid contamination detection: Protect DNA and RNA samples to ensure downstream accuracy
How the NanoDrop One UV-Vis Spectrophotometer is bringing specificity to UV-Vis measurements
11 Nov 2020

A new solution from Thermo Fisher Scientific is now available to help scientists determine the purity of their DNA or RNA sample by detecting nucleic acid contamination using UV-Vis.
Nucleic acid contamination of your DNA or RNA samples can be detrimental to the accuracy of downstream experimental results, whether that be qPCR, RT PCR sequencing or any other assay. Here, SelectScience speaks with Patrick Brown, Product Manager, NanoDrop Microvolume UV-Vis, Thermo Fisher Scientific, to learn more about the new nucleic acid contamination detection software upgrade available for the Thermo Scientific™ NanoDrop™ One UV-Vis Spectrophotometer and how this can transform your research by providing confidence in your results.
Bringing specificity to UV-Vis
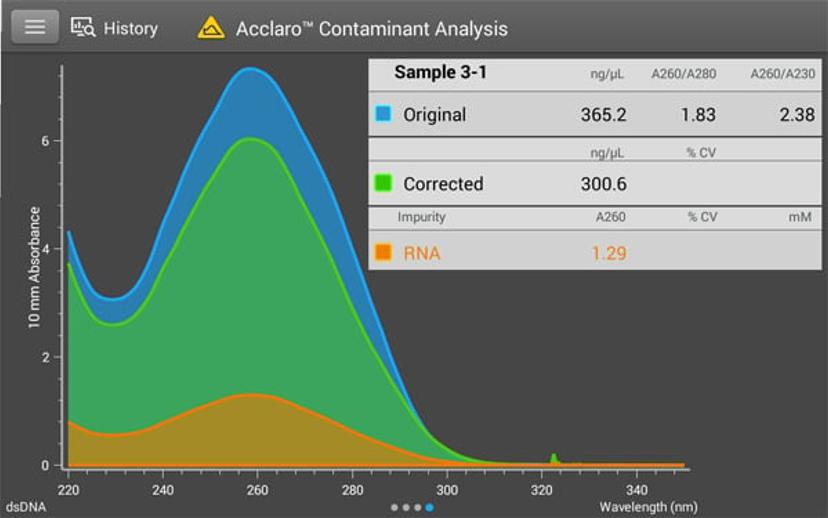
UV-Vis instruments enable scientists to quantify nucleic acid concentration following DNA or RNA extraction. However, during this quality control step, the UV-Vis instrument measures the entire absorbance of the sample. As a result, undetected nucleic acid contamination – RNA contamination in DNA or DNA contamination in RNA – can result in an overestimation of the concentration of the nucleic acid of interest. This contamination can consequently result in the incorrect amount of input DNA or RNA being used in downstream assays, which can lead to unreliable assays results.
If you are concerned about DNA or RNA contamination in your samples, traditional practices require the use of fluorescence assays to determine the specific concentration of each nucleic acid in your sample. While fluorescence assays may be the gold standard for measuring relative DNA and RNA concentrations in your sample, they require sample preparation, generation of a standard curve and incubation time. UV-Vis analysis in comparison requires just 1-2 µL of undiluted sample, but the ability to distinguish RNA from DNA using UV-Vis has been challenging as both nucleic acids are also absorbed at similar wavelengths. However, with the latest software update for the NanoDrop One UV-Vis spectrophotometer, users can now determine accurate DNA and RNA measurements from their sample at the same time using the same instrument.
NanoDrop users have eagerly awaited this new feature. “Everyone has been excited about the possibilities,” says Brown. The increase in specificity enables scientists to gain confidence in the purity of their samples as well as increase productivity. “The goal with this new ability to assess nucleic acid contaminants is to not only provide customers with an understanding of their sample concentration,” Brown explains, “but also some understanding of the purity of the sample.”
How does it work?
“We're taking the first step to providing nucleic acid specificity in a UV-Vis measurement by introducing mathematical models that can differentiate the absorbance spectrum of DNA from RNA,” says Brown. With the latest update of the NanoDrop software, its Thermo Scientific™ Acclaro™ Sample Intelligence technology algorithms are now able to identify RNA and DNA contamination, in addition to quantifying sample concentration. The technology, which works for samples of mammalian origin, provides information on the percentage makeup of a given sample – for example, if a sample contains 25% DNA and 75% RNA. This measurement is then used to produce a DNA or RNA concentration based on the uncorrected value.
“What we find is that our predictive software is able to provide a much more accurate concentration value than just the raw absorbance value,” says Brown. “So, we can get much better data, when we apply these algorithms.” After becoming aware of DNA or RNA contamination, users can then decide if they need to further process their sample or if the value is acceptable for downstream experiments.
Reduce troubleshooting – saving time & money
In addition to removing the need to perform fluoresce assays, a key advantage of the NanoDrop spectrophotomer’s new nucleic acid contamination detection feature is that it will eliminate troubleshooting in downstream assays. For example, if insufficient DNA or RNA is used in a reaction, detection early on will save users time, money, and enable them to get to important end results faster. “By providing a corrected concentration, users can be successful the first time and not have to spend hours redoing the experiment nor spend hundreds, maybe thousands of dollars in reagent costs to repeat that experiment,” Brown highlights.
How do I get the software update?
The software update is available as a free download for all Nanodrop One instrument owners. “Even if you purchased your instrument three years ago, you can go to the Thermo Fisher Scientific website and download this new feature for free,” Brown concludes.
Learn more about the latest updates to the NanoDrop in this SelectScience webinar>>

