Quick and Accurate Assessment of CNS Neuroinflammation
2 May 2017
Neuroinflammation is a common feature of many diseases of the central nervous system (CNS), including neurodegenerative disorders. A combination of responses from neurons, microglia, astrocytes and peripheral immune cells along with cytokines, chemokines and the complement system constitute the basis for neuroinflammation.
BioLegend offers multiple solutions to assess inflammation in the CNS:
- Assess immune cell activation
- Quantitate the levels of inflammatory mediators
- Evaluate cell death
- Detect synaptic loss and neuronal degeneration
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining using a range of specific cellular markers is a technique which allows important insights into neurological tissue samples. Read on for examples of applications of this technique in neuroinflammation research and the types of cellular markers which could be used for each application.
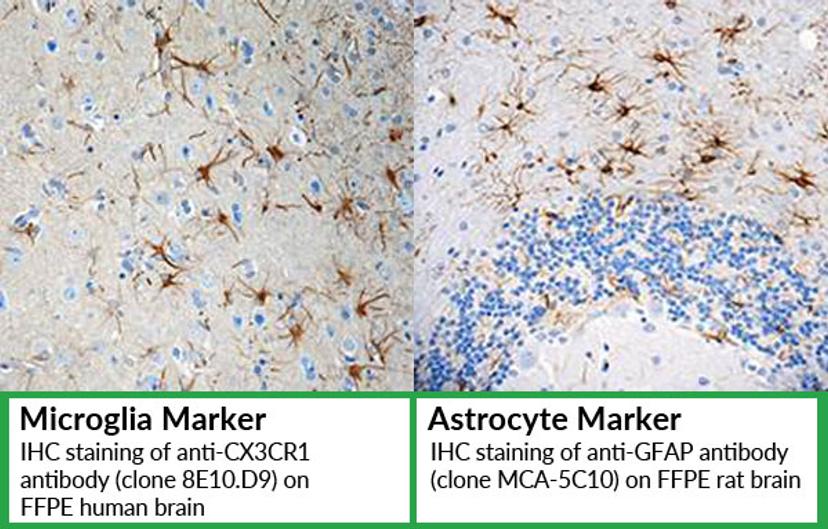
Analysis of cellular phenotype and location
Immunohistochemistry staining with specific cellular markers can be used to detect microglia and astrocytes. These markers allow analysis of cellular phenotype and assessment of cellular location.
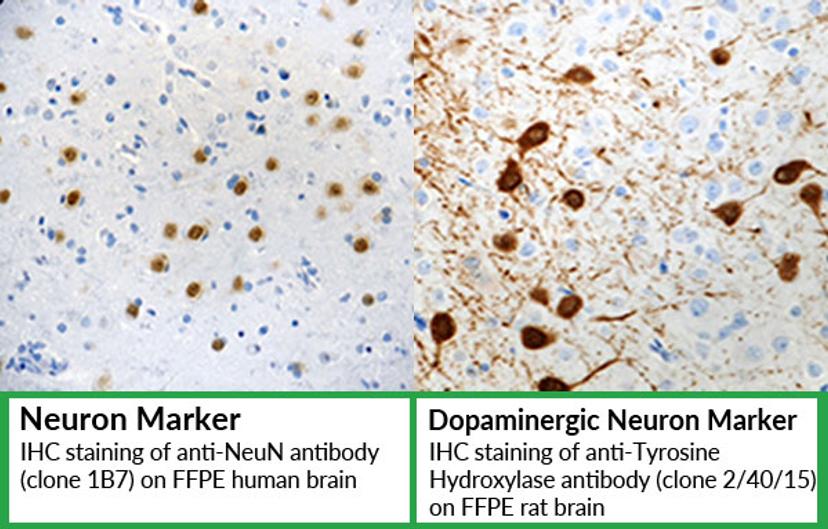
Detection of neuronal loss
Detect neuronal loss using IHC and antibodies that are commonly used as specific neuronal cell markers;
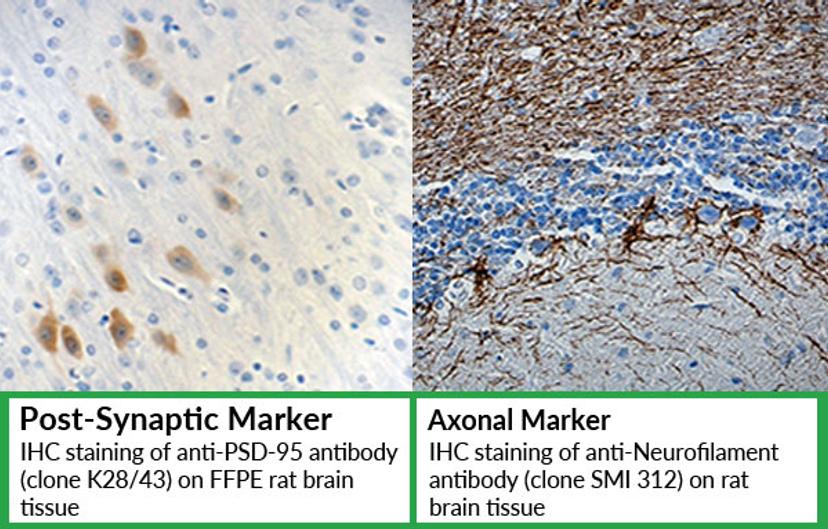
Assessment neuronal and synaptic integrity
Antibodies that are suitable for visualization of synapses, axons and dendrites to be used to assess neuronal and synaptic integrity in tissue sections and cell culture models.