Products & ReviewLife Sciences
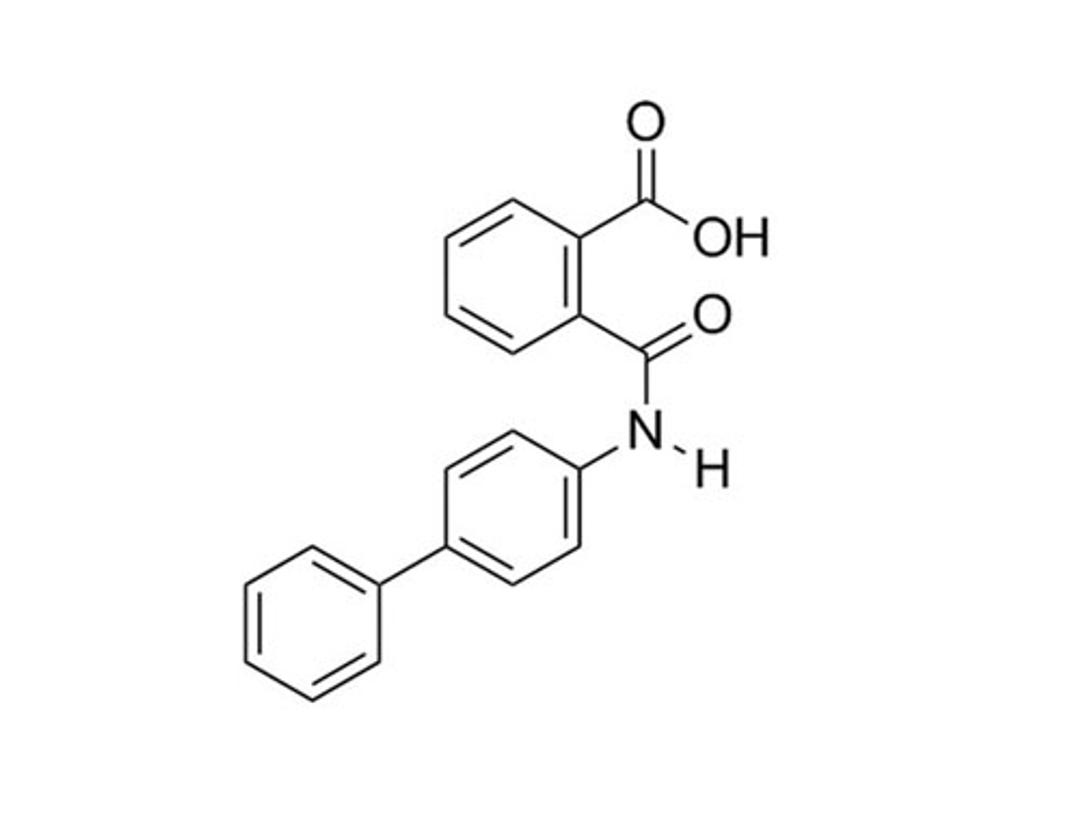
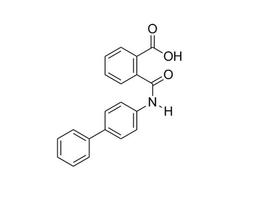
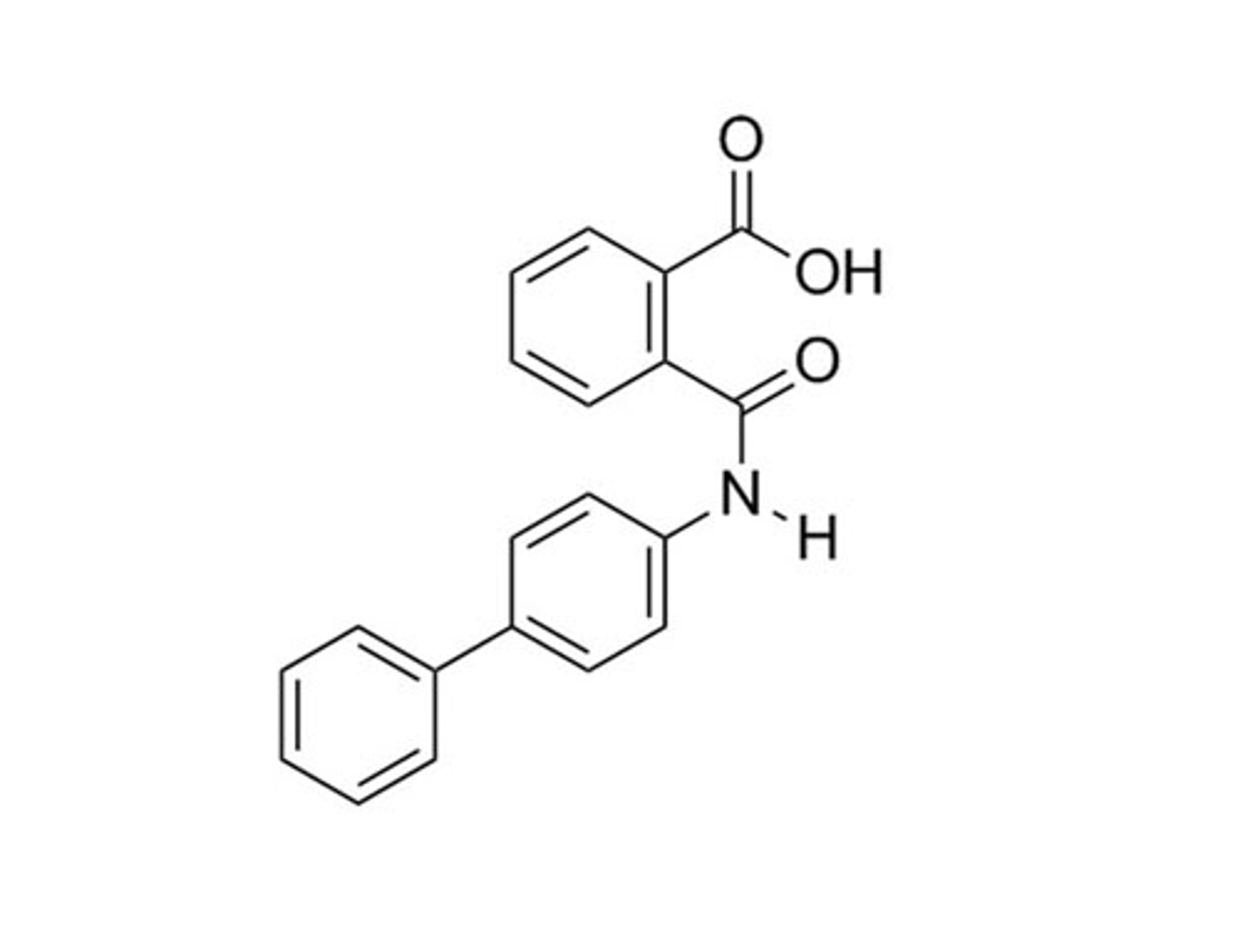
Kartogenin
RUNX1 transcriptional activator; Binds filamin A

The supplier does not provide quotations for this product through SelectScience. You can search for similar products in our Product Directory.
Kartogenin induces chondrogenesis by binding the actin-binding protein, filamin A, which disrupts its interaction with the transcription factor core-binding factor β subunit (CBFβ). When dissociated from filamin A, CBFβ translocates to the nucleus and forms a transcriptional complex with the runt-related transcription factor RUNX1, which enables chondrocyte differentiation (Johnson et al.).
DIFFERENTIATION
- Promotes differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes (Johnson et al.; Zhang et al.)
- Promotes cartilage formation/repair in mouse models of osteoarthritis or when injected into mouse tendon-bone junctions (Johnson et al.; Zhang et al.)
- Promotes type-I collagen synthesis in human dermal fibroblasts in vitro and in the dermis of mice through activation of the SMAD4/SMAD5 pathway (Wang et al.).