RapID™ ONE System
Identify over 70 medically important, oxidase-negative, gram-negative bacilli in just four hours using the Thermo Scientific™ RapID™ ONE System, an identification system based on enzyme technology. The RapID ONE System is a qualitative micromethod employing conventional and chromogenic substrates for the identification of medically important Enterobacteriaceae and other selected oxidase-negative, Gram-negative bacilli is…
Love having these around for Rapid identification
Microbiology Identification
These products are easy to use and very helpful in a small lab.
Review Date: 23 May 2022 | Thermo Fisher Scientific
Identify over 70 medically important, oxidase-negative, gram-negative bacilli in just four hours using the Thermo Scientific™ RapID™ ONE System, an identification system based on enzyme technology.
The RapID ONE System is a qualitative micromethod employing conventional and chromogenic substrates for the identification of medically important Enterobacteriaceae and other selected oxidase-negative, Gram-negative bacilli isolated from human clinical specimens.
- One-step inoculation—decreased prep time for increased productivity
- Manual microbial identification made easy—no oil, no pipetting, no 24-hr incubation
- Four-hour incubation*—quicker time-to-result for a faster response
- Common procedure—lessened materials usage saves time and money
- Visible color reactions—reduced subjectivity decreases repeat testing
- Better reporting—more coverage, advanced updates
- *Two-hour incubation for RapID SS/u.
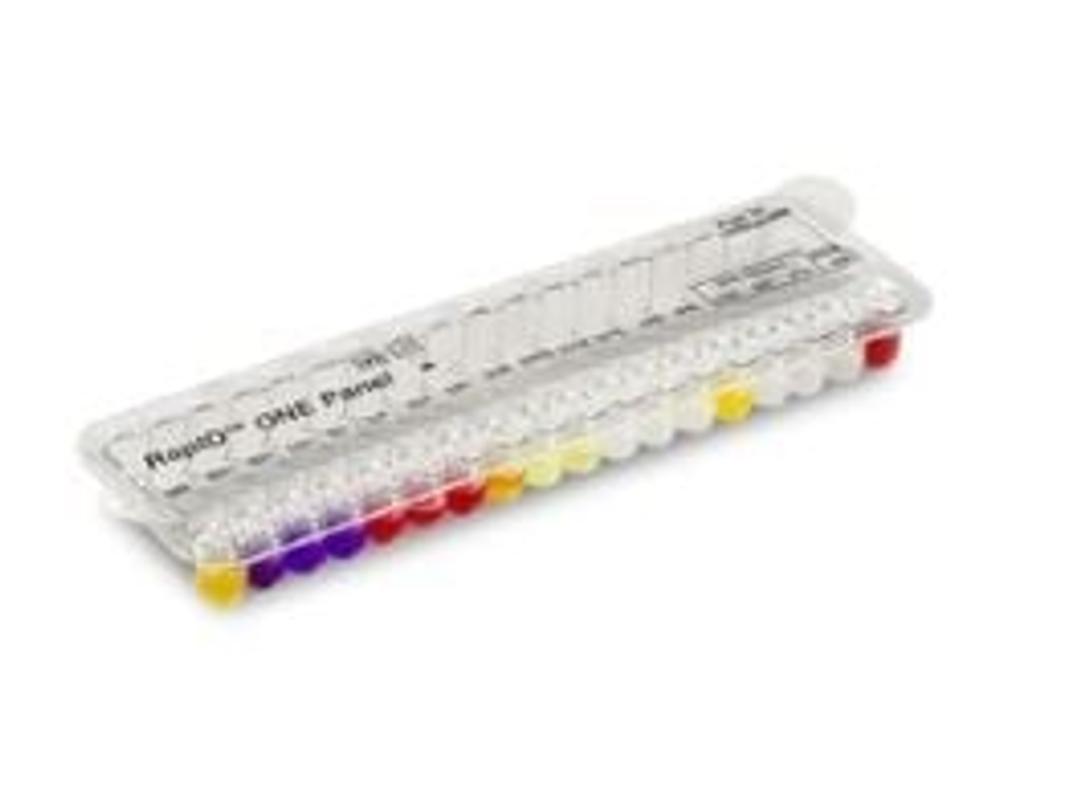
A clear plastic tray contains reagent impregnated wells, allowing simultaneuos inoculation of each cavity with a predetermined volume of inoculum. A suspension of test organism in RapID Innoculation Fluid is used as the inoculum which rehydrates and initiates test reactions.
After incubation, each cavity is examined for reactivity by noting the development of a color. In some cases, reagents must be added to the cavities to provide a color change. The resulting pattern of positive and negative scores is used as the basis for identification of the test isolate by comparison of test results to reactivity patterns stored in a databse or through the use of a computer-generated Code Compedium (ERIC).