Products & ReviewLife Sciences
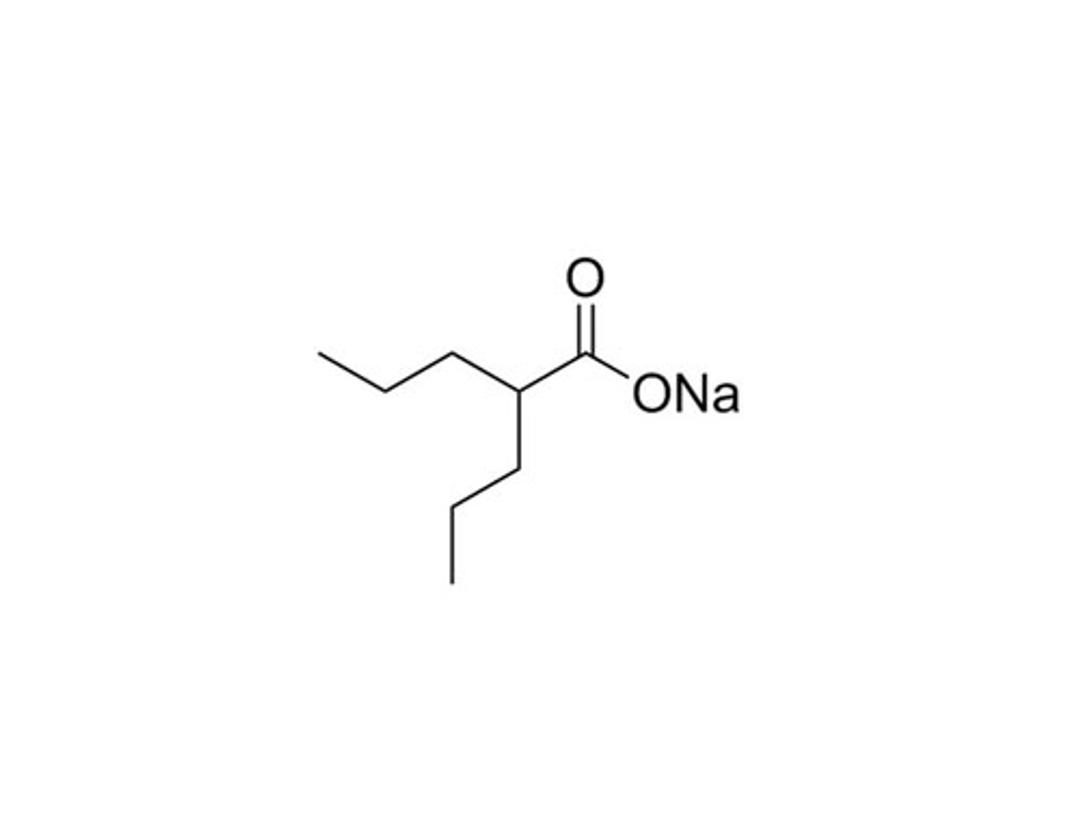
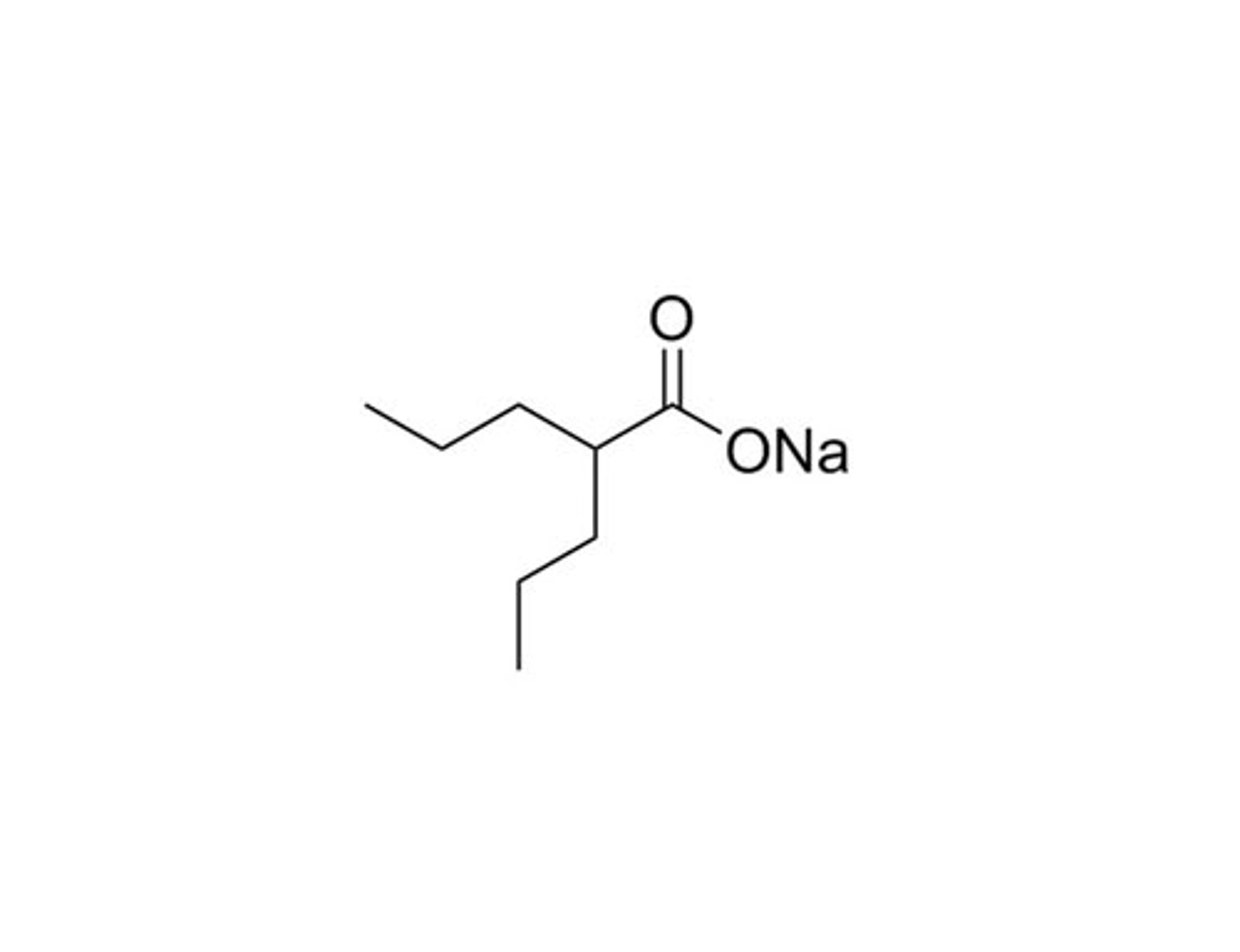
Valproic Acid
Epigenetic modifier; Inhibits histone deacetylase (HDAC)1

The supplier does not provide quotations for this product through SelectScience. You can search for similar products in our Product Directory.
Valproic Acid (VPA) is a short-chain fatty acid that acts as an epigenetic modifier by inhibiting Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) with IC₅₀ values ranging from 0.4 - 3 mM. VPA can also increase γaminobutyric acid (GABA) levels via inhibition of enzymes involved in GABA metabolism. Other effects include depletion of cellular inositol by inhibiting myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase. (Gottlicher et al., Khan et al., Phiel et al., Rosenberg)
REPROGRAMMING
- Enables chemical reprogramming (without genetic factors) of mouse embryonic fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, in combination with CHIR99021, Forskolin, Tranylcypromine, 3-Deazaneplanocin A, and E-616452 (Hou et al.).
- Increases the reprogramming efficiency of mouse embryonic fibroblasts to iPS cells (Huangfu et al. 2008a).
- Promotes reprogramming of human fibroblasts to iPS cells using only 2 factors, OCT4 and SOX2 (Huangfu et al. 2008b).
- Direct lineage reprogramming of fibroblasts to mature neurons, in combination with CHIR99021, RepSox, Forskolin, SP600125, Gö6983 and Y-27632 (Hu et al.).
MAINTENANCE AND SELF-RENEWAL
- Mediates ex vivo expansion of cord blood CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (Chaurasia et al.).
- Promotes the proliferation and self-renewal of human and mouse hematopoietic progenitor cells (Bug et al., De Felice et al.).
DIFFERENTIATION
- Promotes differentiation of neurons and suppresses differentiation of astrocytes and oligodendrocytes from rat neural progenitor cells (Hsieh et al., Jung et al.).
- Promotes osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells (Cho et al.).