Anti-Opsin Antibody, Red/Green
Product Details
- Cat. No.
- AB5405
- Type
- Primary Antibody
- Clonality
- Polyclonal
- Host
- Rabbit

The supplier does not provide quotations for this antibody through SelectScience. You can search for similar antibodies in our Antibody Directory.
Description
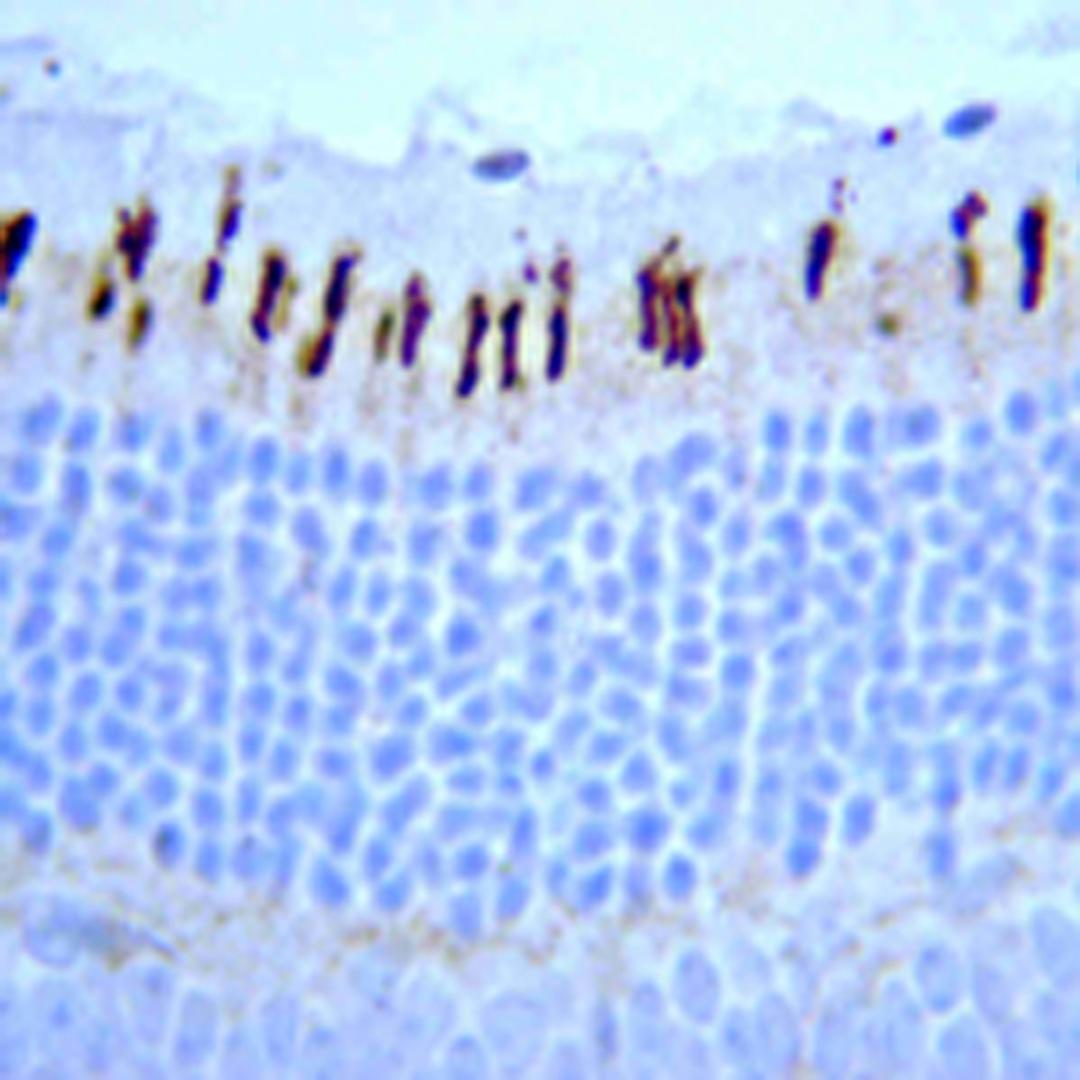
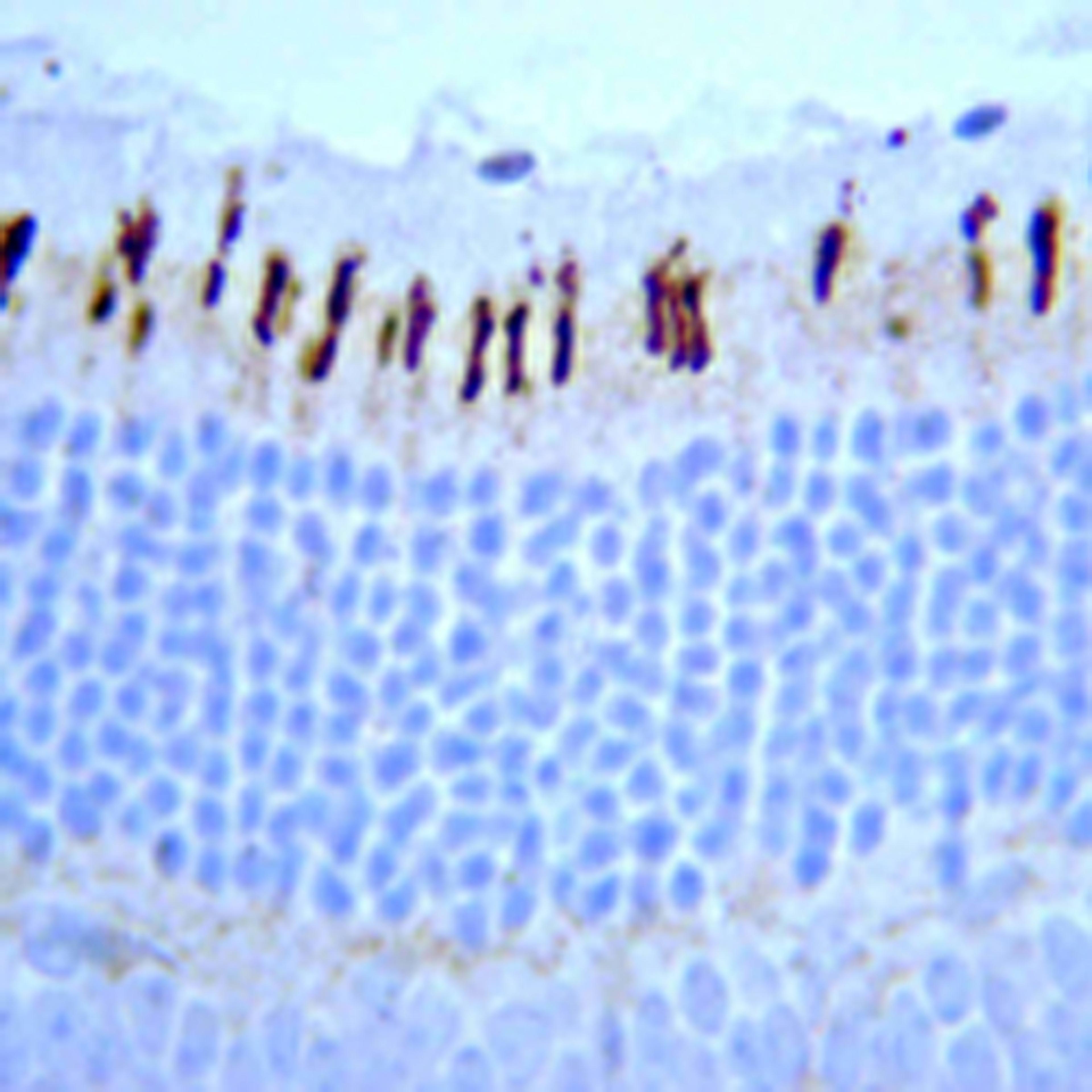
The full range of color discrimination in humans is based on the presence and function of three cone photoreceptor mechanisms. Each cone type possesses a photo-sensitive pigment-protein complex consisting of 11-cis retinal and a unique opsin protein, which gives sensitivity in the short (S cone, peak sensitivity about 420nm), middle (M cone, peak sensitivity about 530nm with polymorphism; Winderckx et al., 1993; Neitz & Neitz, 1998), and long (L cone, peak sensitivity about 560nm with polymorphism; Neitz & Jacobs, 1990) wavelengths of the light spectrum. All three opsins are transmembrane proteins with seven membrane-spanning regions. Genes for the three types of cone opsins and the rod photoreceptor rhodopsin gene seem to be homologous with varying amounts of conservation. Strongest conservation is between the middle (green) and long (red) wavelength sensitive pigments on the X chromosome, suggesting a relatively recent duplication/divergence event (Nathans, 1989; Nathans et al., 1992). The S cone (blue) opsin is located on chromosome 7 and seems to have stronger conservation with rhodopsin. Cone photoreceptor distribution in humans is dominated by the M and L cone pigments
Biological Information
- Clonality: Polyclonal
- Host: Rabbit
- Reactivity: Human, Monkey, Mouse
Handling
- Specificity: 5
Applications
- Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin-Embedded Sections) (IHC (P))
Works well without much variability.
Immunohistochemistry
Easy to use and able to achieve high quality results.
Review Date: 2 Jun 2020 | Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany