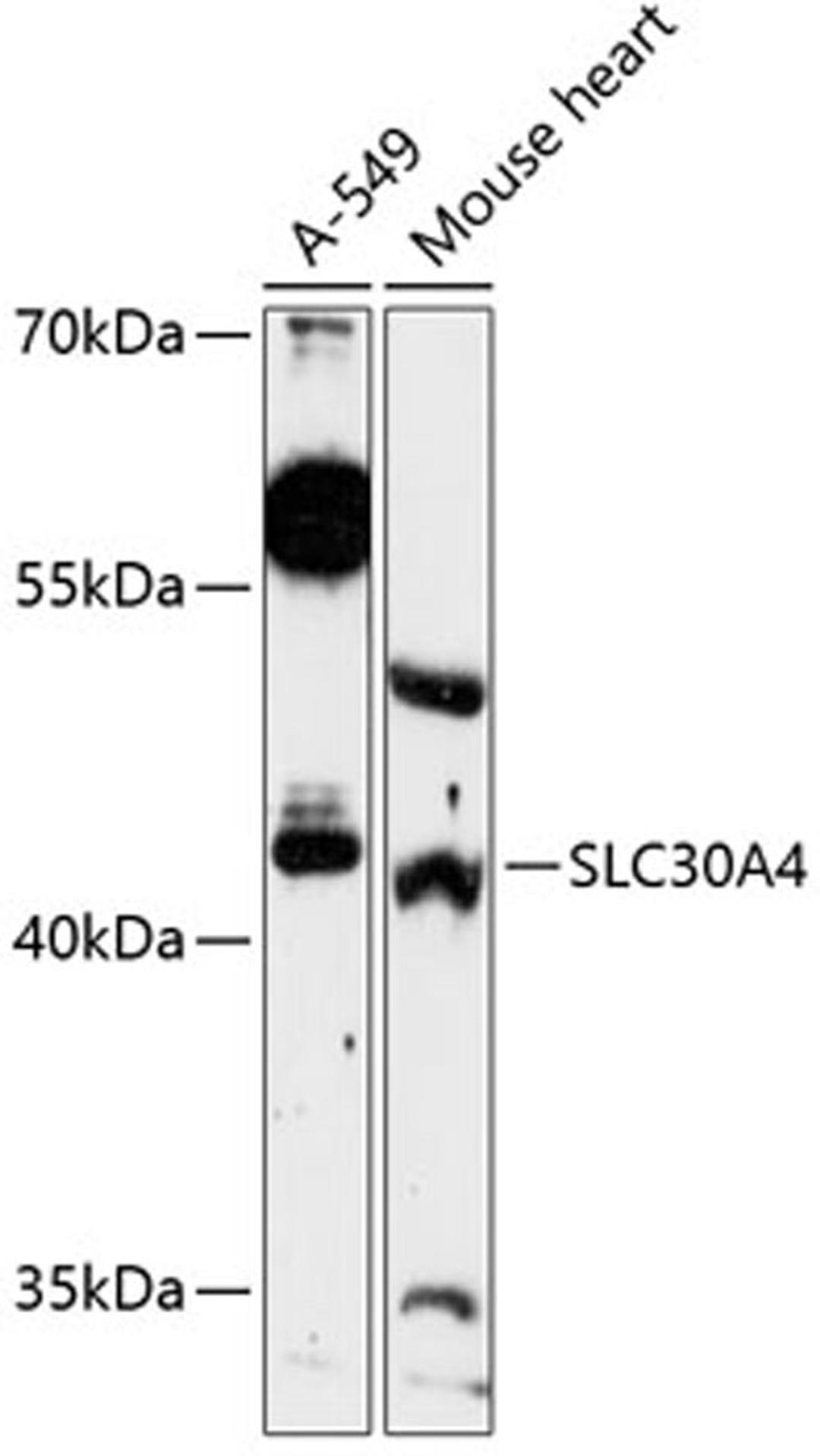
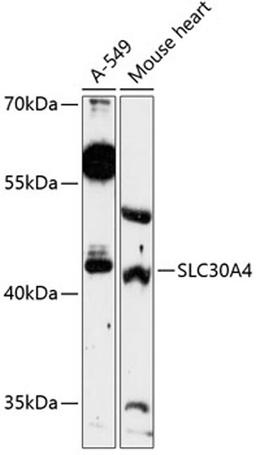
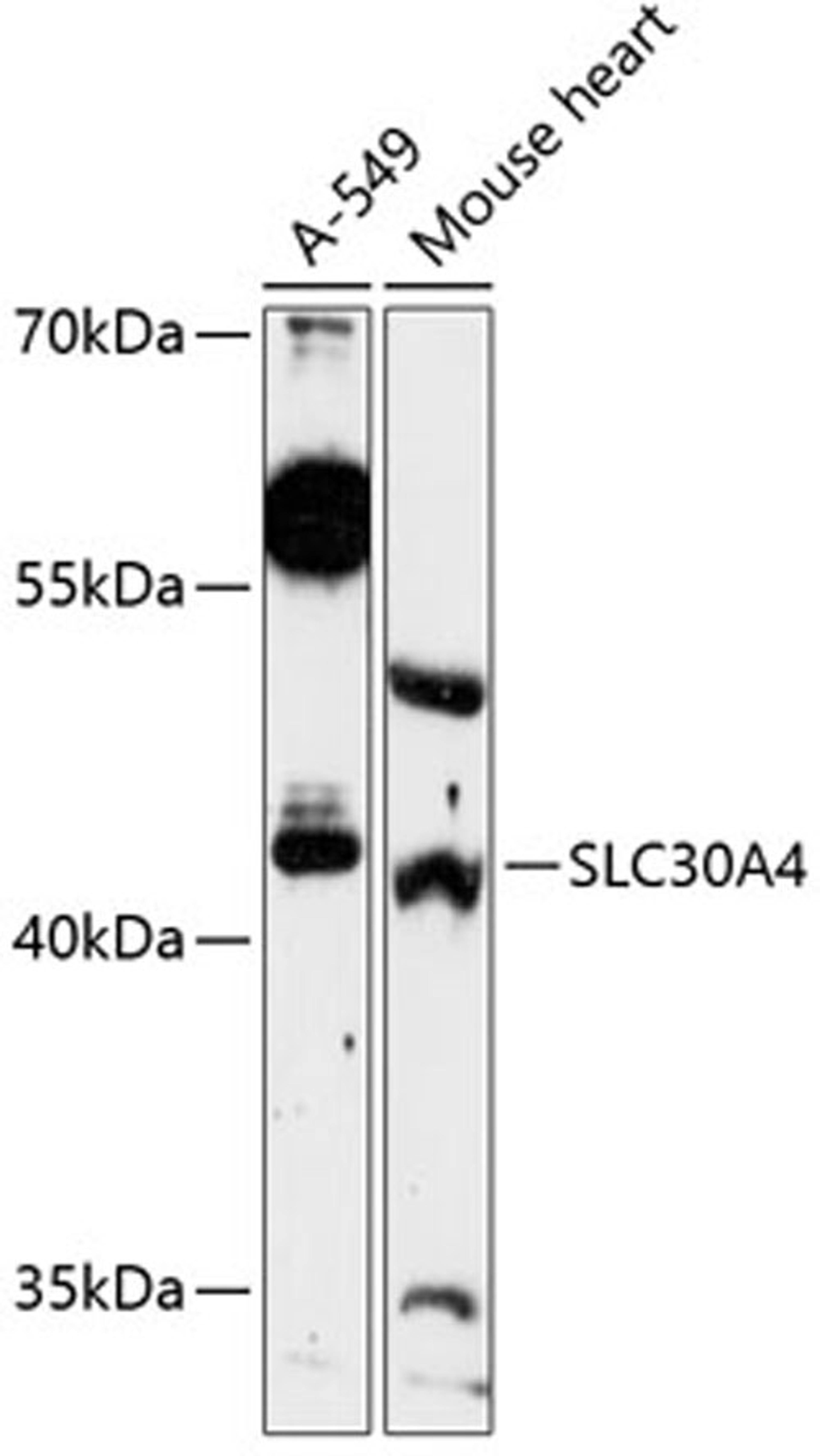
Zinc is the second most abundant trace metal in the human body. It is an essential element, serving both a structural role, as in the formation of zinc fingers in DNA-binding proteins, and a catalytic role in metalloenzymes, such as pancreatic carboxypeptidases (e.g., MIM 114852), alkaline phosphatases (e.g., MIM 171760), various dehydrogenases, and superoxide dismutases (e.g., MIM 147450). SLC30A4, or ZNT4, belongs to the ZNT family of zinc transporters. ZNTs are involved in transporting zinc out of the cytoplasm and have similar structures, consisting of 6 transmembrane domains and a histidine-rich cytoplasmic loop (Huang and Gitschier, 1997 [PubMed 9354792]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]
- Clonality: Polyclonal
- Host: Rabbit
- Reactivity: Human, Mouse