Acoustic Dispensing for High Throughput Single Cell Sequencing Workflows
Improving RNA single cell genomics and sequencing library preparation protocols
9 Apr 2017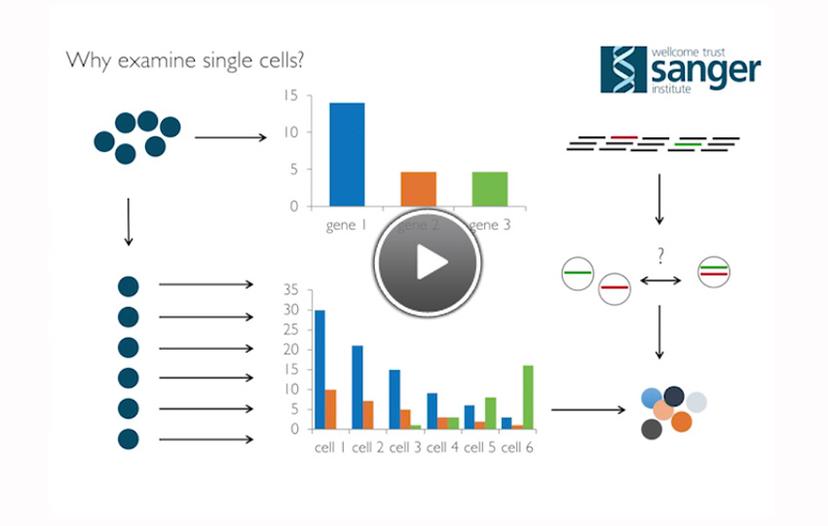
A slide from Dr. Stepham Lorenz's presentation for Labcyte Genomics Symposium 2016

The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute is one of the premier centers of genomic discovery and understanding in the world. The Institute is part of the Wellcome Genome Campus located in Cambridge, UK. The Single Cell Genomics Core Facility there provides a transcriptome, genome and methylome sequencing service to the Wellcome Sanger Facility and their collaborators.
Dr. Stephan Lorenz, Head of the Single Cell Genomics Core Facility at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, UK was filmed speaking at the Labcyte Genomics Symposium. Dr. Lorenz explains the importance of single cell analysis versus cell population studies for obtaining better discrimination of individual gene expression within a population. In this way, it is possible to answer questions that bulk cell population methods are not able to discern.
Dr. Lorenz provides an overview of the workflows used at the facility for isolating cells, amplifying RNA and DNA, library preparation and sequencing. He discusses cell capture including laser capture from tissue, cell dissociation and cell sorting. Dr Lorenz focuses on RNA sequencing for single cell genomics, in particular library preparation protocols.
The technology is showcased using a mouse embryonic stem cell study that investigated the subpopulation structure and the effects of different induced cell differentiation and pluripotency stages on the heterogeneity of gene expression. Dr. Lorenz illustrates how single cell transcriptome sequencing increases the resolution and enables cycling of cells between distinct developmental subpopulations to be observed. In contrast, an average reading of the population will not differentiate between the different cell states within a sample.
Streamlining RNA library construction
Focusing primarily on RNA, Dr. Lorenz describes, in detail, standard library construction steps and how they have streamlined them to increase productivity. After isolating cells into 96- or 384-well plates, reverse transcription of single cell RNA and amplification is carried out. This is followed by clean-up and then library construction, converting cDNA into sequencing ready libraries. A template switching, Smart-seq protocol is used at the core facility that produces amplified sequences with universal handles incorporated at either end. Dr. Lorenz describes how they have incorporated semi-automated liquid handling reverse transcription that is rapid, RNAse free easy-to-use and incorporates cDNA quality control (QC) monitoring.
Automated solid phase reversible immobilization (SPRI) clean-up is followed by sample transfer using Labcyte Echo liquid handling and Access systems for quantification, normalization and library construction.
Dr. Lorenz presents data demonstrating how acoustic liquid handling reliably transfers DNA with wide ranging sizes and concentrations. He also describes how the technology can routinely quantify eight 384-well plates, in one run with standards and normalization.
The Nextera method for DNA sample preparation
The Nextera method employed at the facility is described. This method involves DNA fragmentation, with addition of a small overhang using transposases, so PCRs can be run with an adapter and primer against the overhangs, which introduces barcodes and flow cell adapters.
Selected for speed, Dr. Lorenz describes how the Nextera protocols have been adapted for the Echo and miniaturized to eliminate issues of high tip consumption and high cost per sample, whilst maintaining the same performance quality. The team are currently extending this to accommodate a 1536-well plate format.
The final stages of library construction prior to sequencing are described, in particular library QC using BioAnalyser qPCR that has been simplified using acoustic liquid handling, to reduce reaction volumes 10-fold, and save time and consumables by further using a simulated serial dilution.
Watch the full presentation or learn more about the Echo® 525 Liquid Handler
Leave a product review today to be entered into a prize draw for the chance to win an iPad or $400 Amazon voucher (or equivalent currency)
