Dopamine
High Quality Assays with Reproducible and Reliable Results

The supplier does not provide quotations for this product through SelectScience. You can search for similar products in our Product Directory.
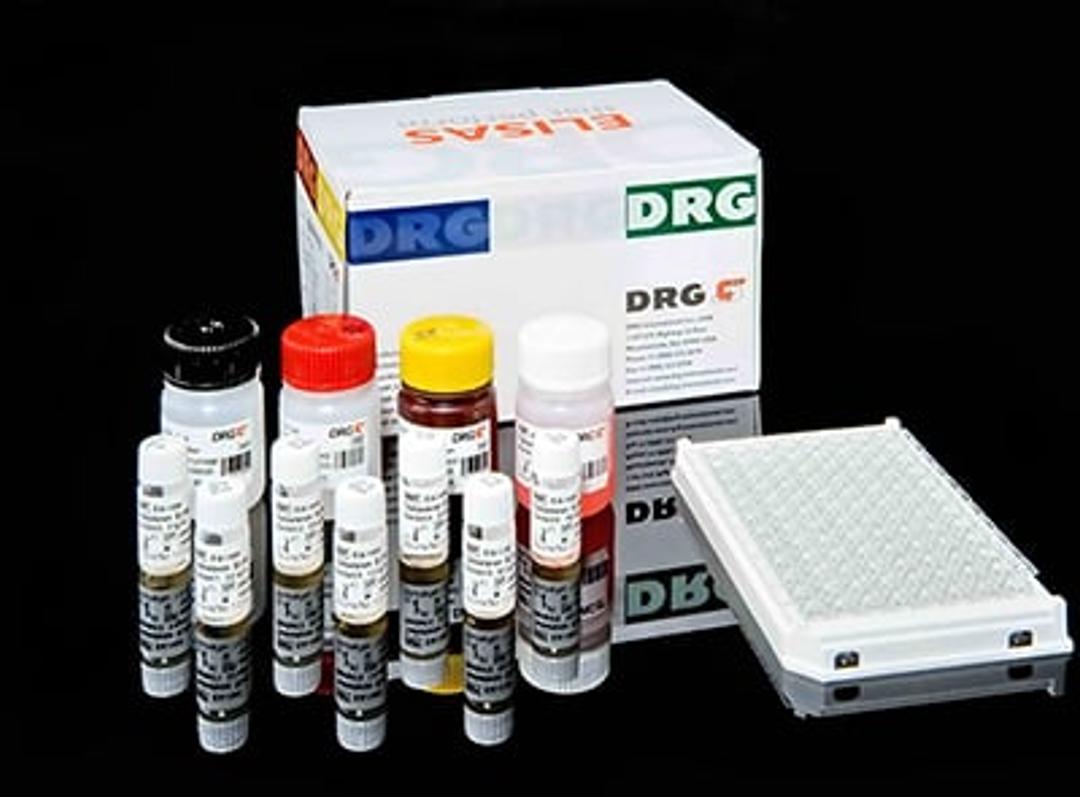
Enzyme Immunoassay for the quantitative determination of dopamine in plasma and urine.Dopamine is extracted by using a cis-diol-specific affinity gel, acylated and then converted enzymatically. The competitive ELISA kit uses the microtiter plate format. The antigen is bound to the solid phase of the microtiter plate. The derivatized standards, controls and samples and the solid phase bound analytes compete for a fixed number of antibody bindingsites. After the system is in equilibrium, free antigen and free antigen-antibody complexes are removed by washing. The antibody bound to the solid phase is detected by an anti-rabbit IgG-peroxidase conjugate using TMB as a substrate. The reaction is monitored at 450 nm. Quantification of unknown samples is achieved by comparing their absorbance with a standard curve prepared with known standard concentrations. In humans the catecholamines adrenaline (epinephrine), noradrenaline (norepinephrine) and dopamine are neurotransmitters of the sympathetic nervous system and are involved in many physiological processes. The sympathetic nervous system sets the body to a heightened state of alert, also called as the body’s fight-or-flight response. In the human body thecatecholamines and their metabolites indicate the adaption of the body to acute and chronic stress. Next to the metanephrine/normetanephrine the catecholamines are important for the diagnosis and the follow-up of tumors of the sympathoadrenal system like the pheochromocytomas. The quantitative determination of catecholamines in urine is preferred for the diagnosis of these tumors, whereas the determination of catecholamines in plasma is medically sensible for the localization of the tumor and for function testing. Values above the cut-off can provide an indication for neuroendocrine tumors. However, in literature various diseases like hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, schizophrenia and manic depression are described with abnormal low or high levels of catecholamines. Therapeutic consequences should never be based on laboratory results alone even if all test results arein agreement with the items as under point “Procedural cautions, guidelines and warnings”. Any laboratory result is only a part of the total clinical picture of the patient. Only in cases where the laboratory results are in an acceptable agreement with the overall clinical picture of the patient it can be used for therapeutic consequences. The test result itself should never be the sole determinant for deriving any therapeutic consequences.