Minocycline
Antibiotic with anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties

The supplier does not provide quotations for this product through SelectScience. You can search for similar products in our Product Directory.
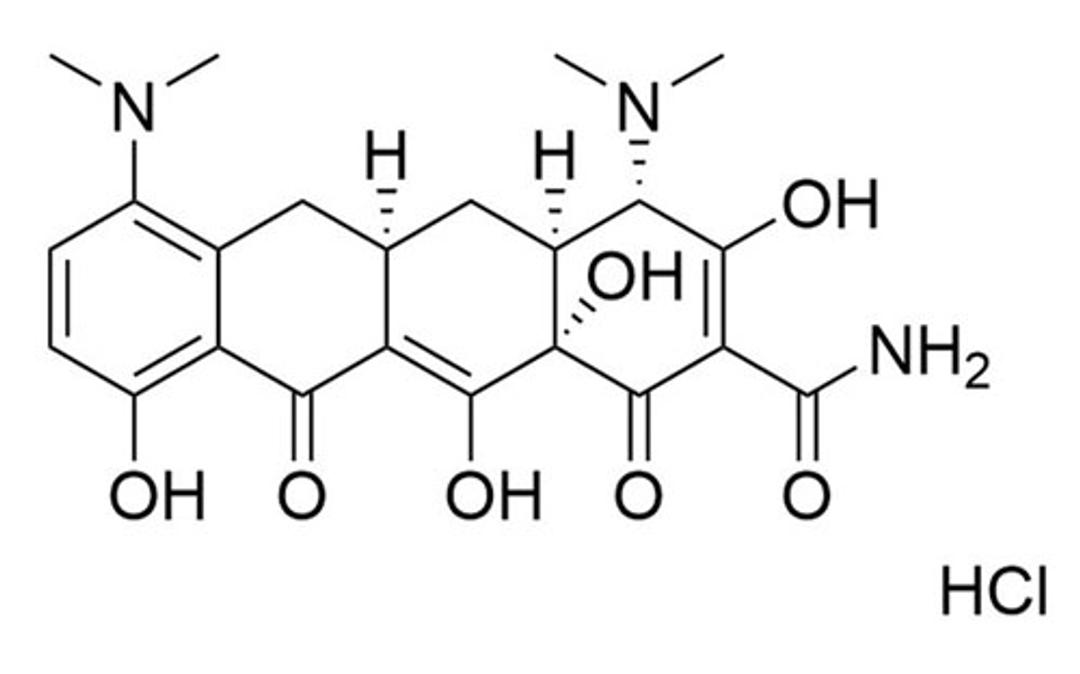
Minocycline is a semi-synthetic tetracycline and antibiotic broadly used to treat various bacterial infections. It inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit. It has also been reported to chelate with Ca2+ and Mg2+ (Lambs et al.). Reported to be anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and neuroprotective (Garrido-Mesa et al.), some of its mechanism of actions include inhibiting enzymatic activities of inducible nitric oxide synthase (Amin et al.), matrix metalloproteinases (Golub et al.), and phospholipase A2 (Pruzanski et al.), inhibiting activation of caspase-1 and caspase-3 (Chen et al.), inhibiting activity of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (Alano et al.), and reduction of p38 MAPK phosphorylation (Corbacella et al.). This product is supplied as the hydrochloride salt of the molecule.
REPROGRAMMING
- Enables derivation of extended pluripotent stem cells from both humans and mice (Yang et al.).
IMMUNOLOGY
- Reduces the production of interleukin-8 elicited by activation of protease-activated receptor 2 in normal human epidermal keratinocytes, thus attenuating the proinflammatory reactions (Ishikawa et al.).
DISEASE MODELING
- Enhances survival of neural stem cells in rat model of Ischemia (Sakata et al.).
- Supports neuroprotective effects in animal models of Parkinson's disease (Du et al.), Huntington's disease (Chen et al.), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Zhu et al.), Alzheimer's disease (Choi et al.), multiple sclerosis (Brundula et al.), and spinal cord injury (Festoff et al.; Garrido-Mesa et al.).
- Reduces bone and cartilage damage in rheumatoid arthritis via inhibition of collagenase and proteinase activity (Greenwald et al.; Arsenis et al.).