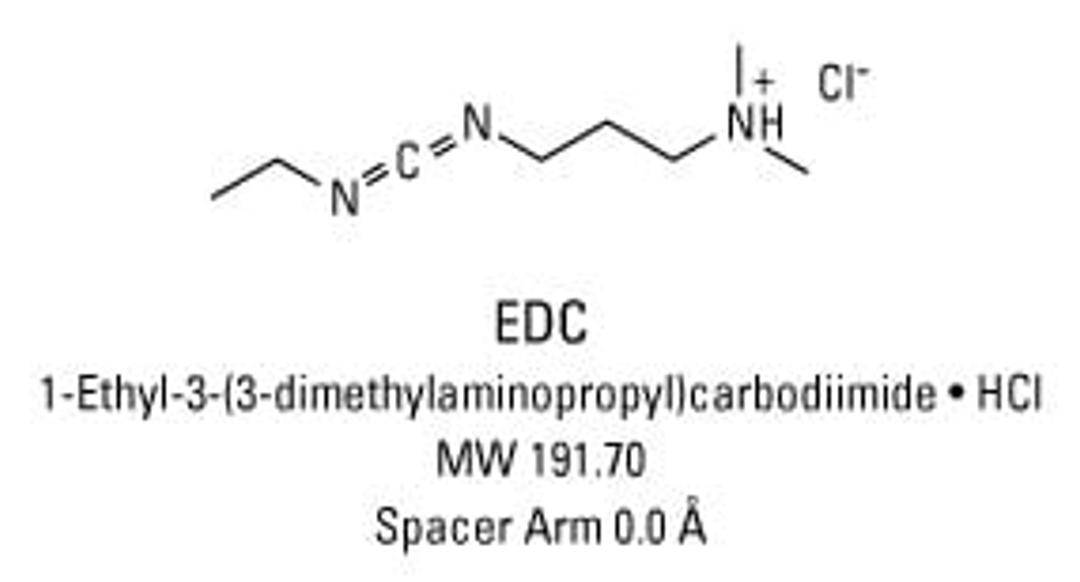
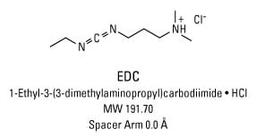
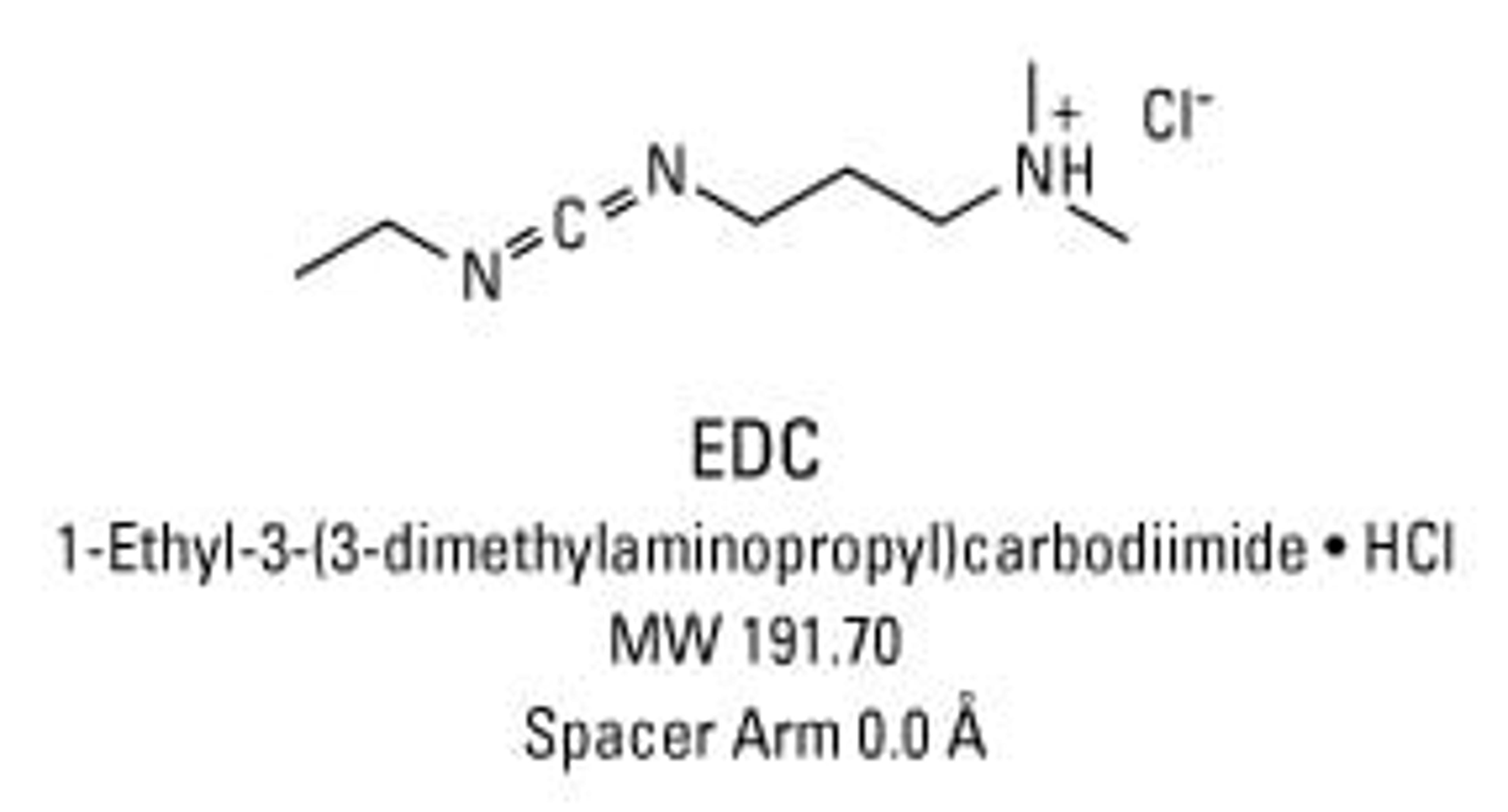
Thermo Scientific™ EDC (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride)
Pierce EDC is a water-soluble carbodiimide crosslinker that activates carboxyl groups for spontaneous reaction with primary amines, enabling peptide immobilization and hapten-carrier protein conjugation.

The supplier does not provide quotations for this product through SelectScience. You can search for similar products in our Product Directory.
Great product
Analysis of cetyl resins
I received a high-quality product and Thermo Fisher always provide good services. and you get shipping fast and on time too.
Review Date: 2 Dec 2022 | Thermo Fisher Scientific
No doubt their solvent is highly recommended for organic chemistry
Organic synthesis
Our lab uses the the chemicals which is exceptionally pure. In organic chemistry, specifically medicinal chemistry, purity is a must.
Review Date: 25 Jun 2021 | Thermo Fisher Scientific
1-Ethyl-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl]carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC or EDAC) is a zero-length crosslinking agent used to couple carboxyl groups to primary amines. This crosslinker has been used in diverse applications such as forming amide bonds in peptide synthesis, attaching haptens to carrier proteins to form immunogens, labeling nucleic acids through 5' phosphate groups and creating amine-reactive NHS-esters of biomolecules. EDC reacts with a carboxyl to form an amine-reactive O-acylisourea intermediate. If this intermediate does not encounter an amine, it will hydrolyze and regenerate the carboxyl group. In the presence of N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide (Sulfo-NHS), EDC can be used to convert carboxyl groups to amine-reactive Sulfo-NHS esters. This is accomplished by mixing the EDC with a carboxyl containing molecule and adding Sulfo-NHS.
Features:
- Several conjugation strategies—react EDC alone with target groups or include NHS or Sulfo-NHS to increase reaction efficiency or to stabilize active intermediate for later reaction to amines
- Neutral linkage—forms neutral amide bonds between carboxyls and amines
- Water-soluble reagent—add directly to reactions in aqueous, physiological buffers
- Soluble reaction byproducts—easily removed by washing with water or dilute acid