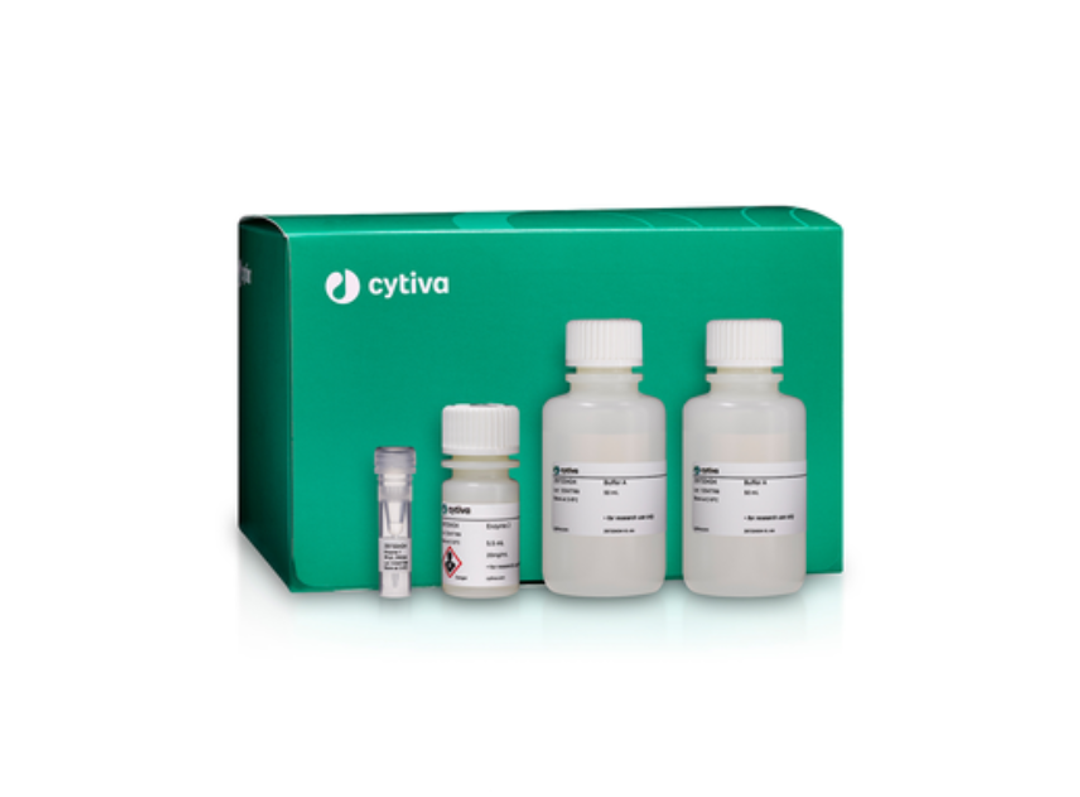
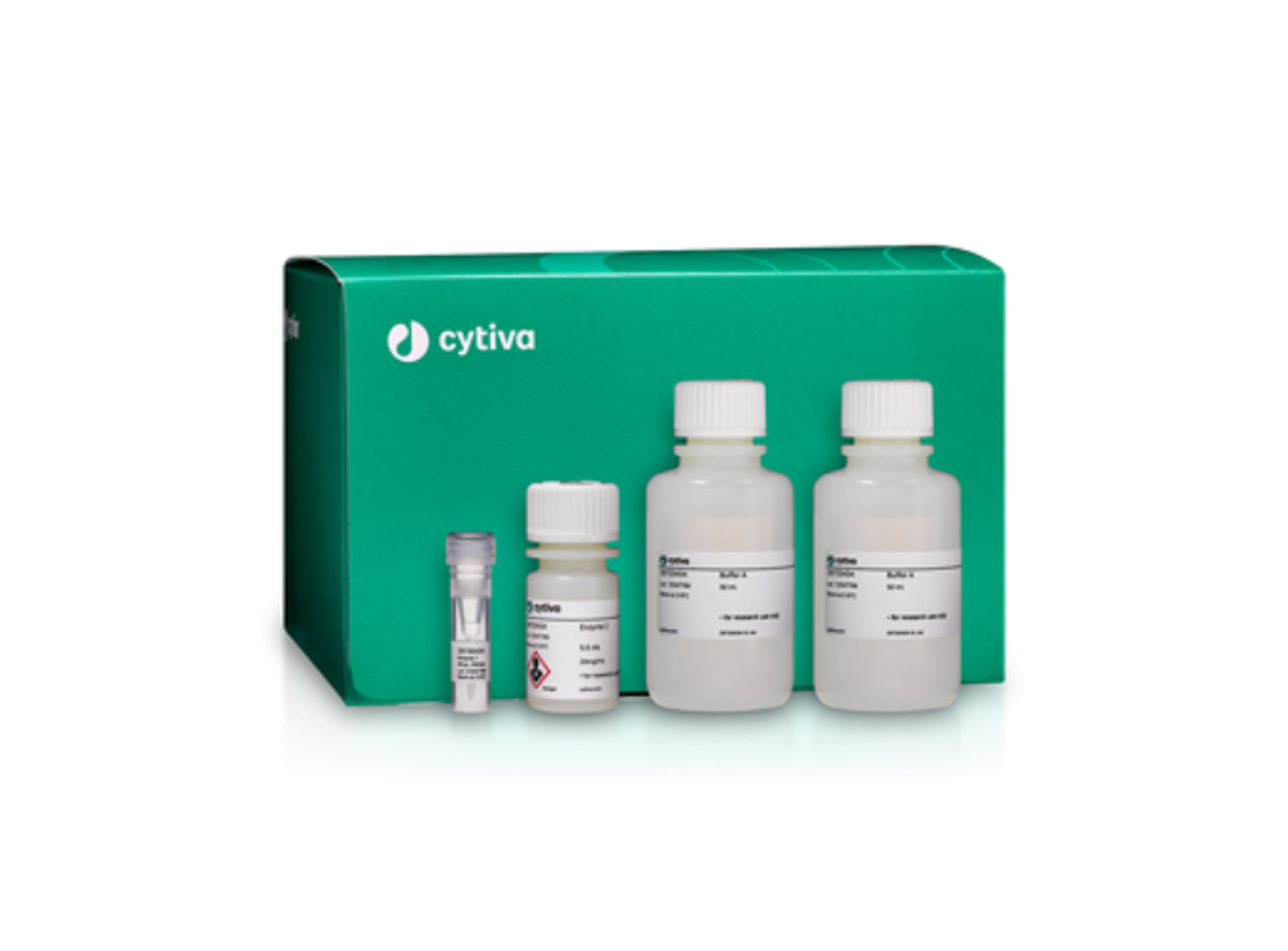
Cold dissociation enzyme mix - kidney
An enzymatic kit for kidney tissue dissociation at 4⁰C, optimized for semi-automated disaggregation in single-cell workflows.

The supplier does not provide quotations for this product through SelectScience. You can search for similar products in our Product Directory.
The Cold Enzyme Dissociation Mix - Kidney* is a standalone kit, intended for the dissociation of kidney tissue in single-cell sequencing. The kit has been optimized for use with semi-automated tissue disaggregation systems.
*For Research Use Only
Works effectively at 4⁰C - Minimized cell death and stress (defined as: apoptosis pathway markers, macrophages, etc.) and improved transcriptional profile of the single cells for more accurate results in single-cell sequencing and analysis.
Ready-made solution specifically for kidney tissue - Optimized for the dissociation of the different segments that are operative in kidney tissue.
Optimized for use with the VIA Extractor™ tissue disaggregator - One of the few systems that can sustain a cold temperature in a controlled manner. Effective dissociation at cooler temperatures increases viability and minimizes cell aggregation.
Single-cell sequencing provides the key to unlocking the origin of renal pathologies at the cellular level, including renal (kidney) carcinomas. One of the first and most critical steps in a single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) protocol is the dissociation of tissues to yield fully-dissociated but intact and viable cells.
Single-cell preparations of the renal tissue are quite cumbersome because the kidney is a complex organ, both functionally and anatomically. Each segment of the kidney is built by very distinct and specialized cell populations.
A limited amount of kidney tissue can be harvested by clinicians as punch biopsies.
Effective enzymatic and mechanical dissociation of kidney tissue is necessary to complete single-cell analysis so that targeted treatments can be developed. Cold-temperature tissue dissociation is popular because it is thought to better preserve the natural transcriptome.