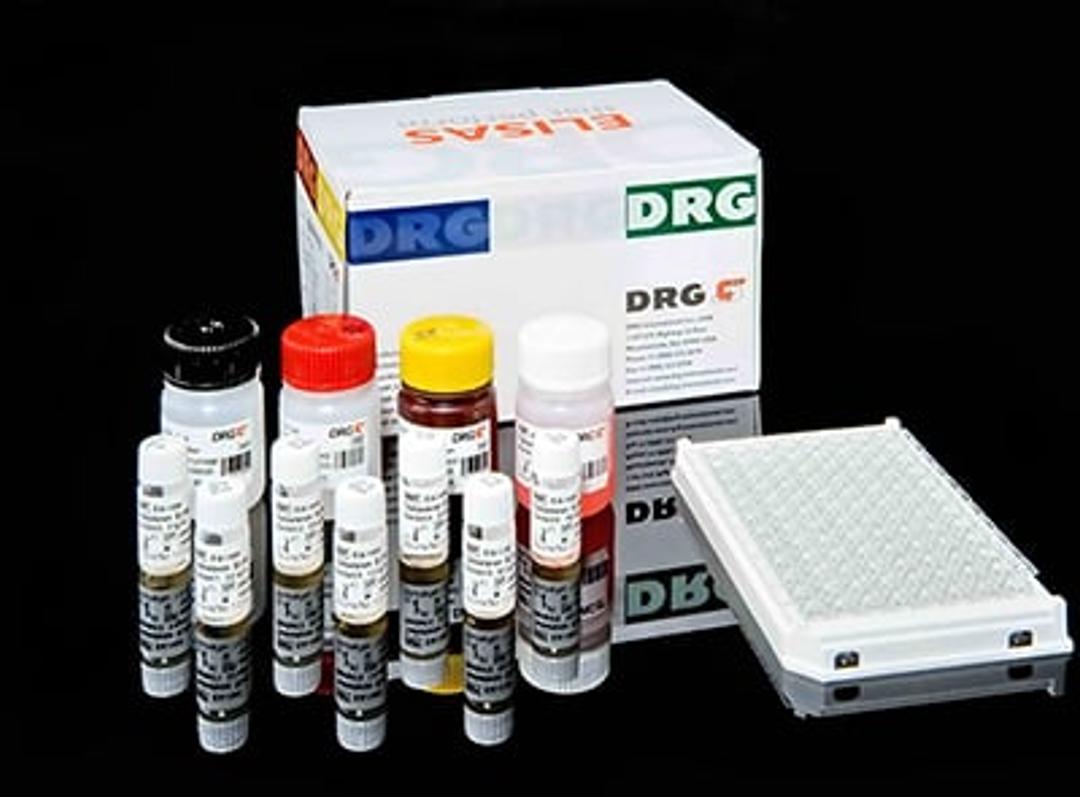
Ureaplasma urealyticum IgA ELISA
High Quality Assays with Reproducible and Reliable Results

The supplier does not provide quotations for this product through SelectScience. You can search for similar products in our Product Directory.
An enzyme immunoassay for the qualitative and semiquantitative determination of IgA-class antibodies to ureaplasma urealyticum in serum and plasma. Ureaplasma urealyticum is a bacterium belonging to the family Mycoplasmataceae. This microorganism is part of the normal genital flora of both men and women. It is found in about 70% of sexually active humans. It can cause disease, including non-specific urethritis (NSU), infertility, chorioamnioitis, stillbirth, premature birth, and, in the perinatal period, pneumonia or meningitis. Especially IgA detection of Ureaplasma urealyticum is useful for the measurement of the acute phase.The DRG Ureaplasma urealyticum IgA ELISA Kit is a solid phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Patient samples are diluted with Sample Diluent and additionally incubated with IgG-RF-Sorbent, containing hyper-immune anti-human IgG-class antibody to eliminate competitive inhibition from specific IgG and to remove rheumatoid factors. This pretreatment avoids false negative or false positive results. Microtiter wells as a solid phase are coated with Ureaplasma urealyticum UreD protein. Diluted patient specimens and ready-for-use controls are pipetted into these wells. During incubation Ureaplasma urealyticum-specific antibodies of positive specimens and controls are bound to the immobilized antigens. After a washing step to remove unbound sample and control material horseradish peroxidase conjugated anti-human IgA antibodies are dispensed into the wells. During a second incubation this anti-IgA conjugate binds specifically to IgA antibodies resulting in the formation of enzyme-linked immune complexes. After a second washing step to remove unbound conjugate the immune complexes formed (in case of positive results) are detected by incubation with TMB substrate and development of a blue color. The blue color turns into yellow by stopping the enzymatic indicator reaction with sulfuric acid. The intensity of this color is directly proportional to the amount of Ureaplasma urealyticum-specific IgA antibody in the patient specimen. Absorbance at 450 nm is read using an ELISA microtiter plate reader.