iCell Hepatocytes
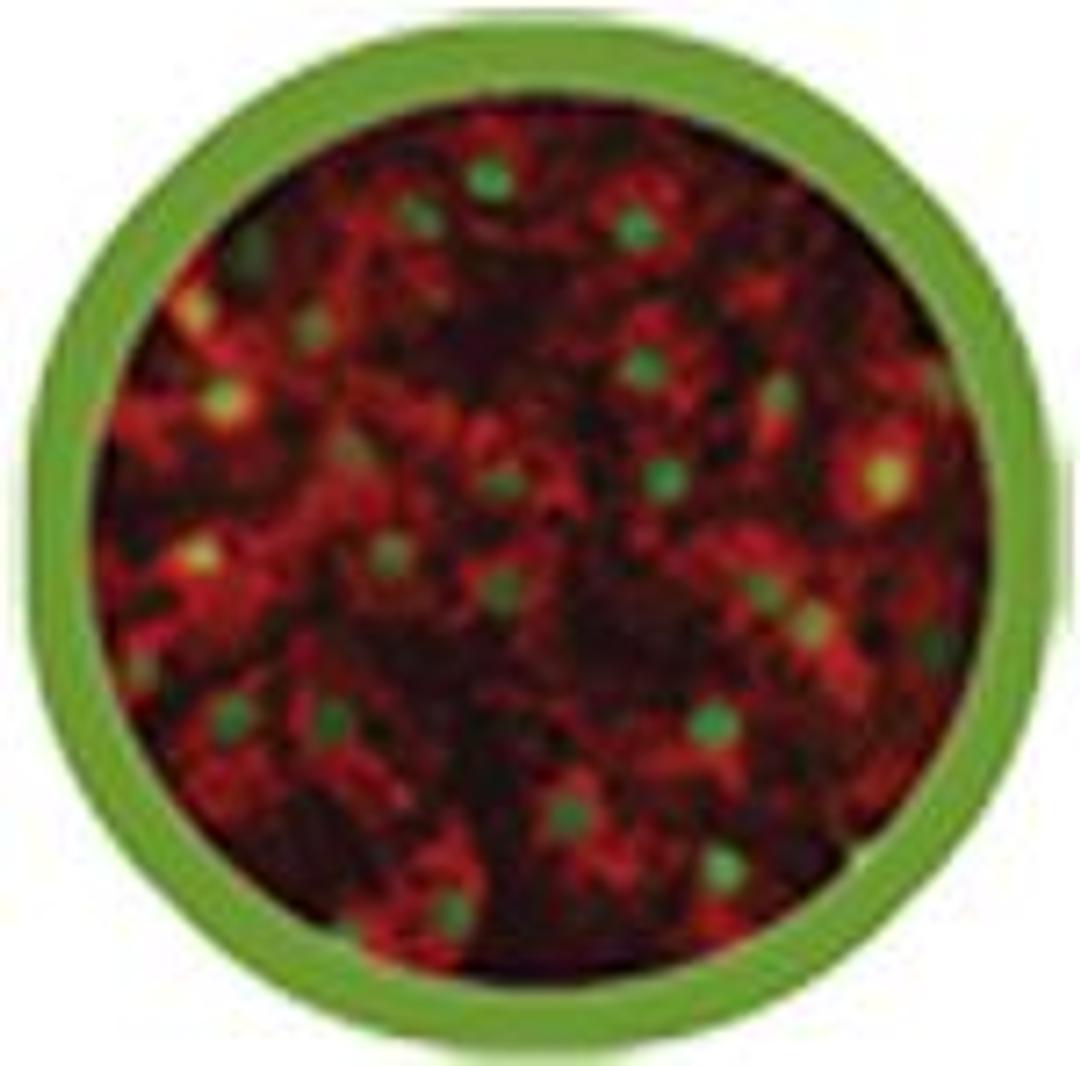
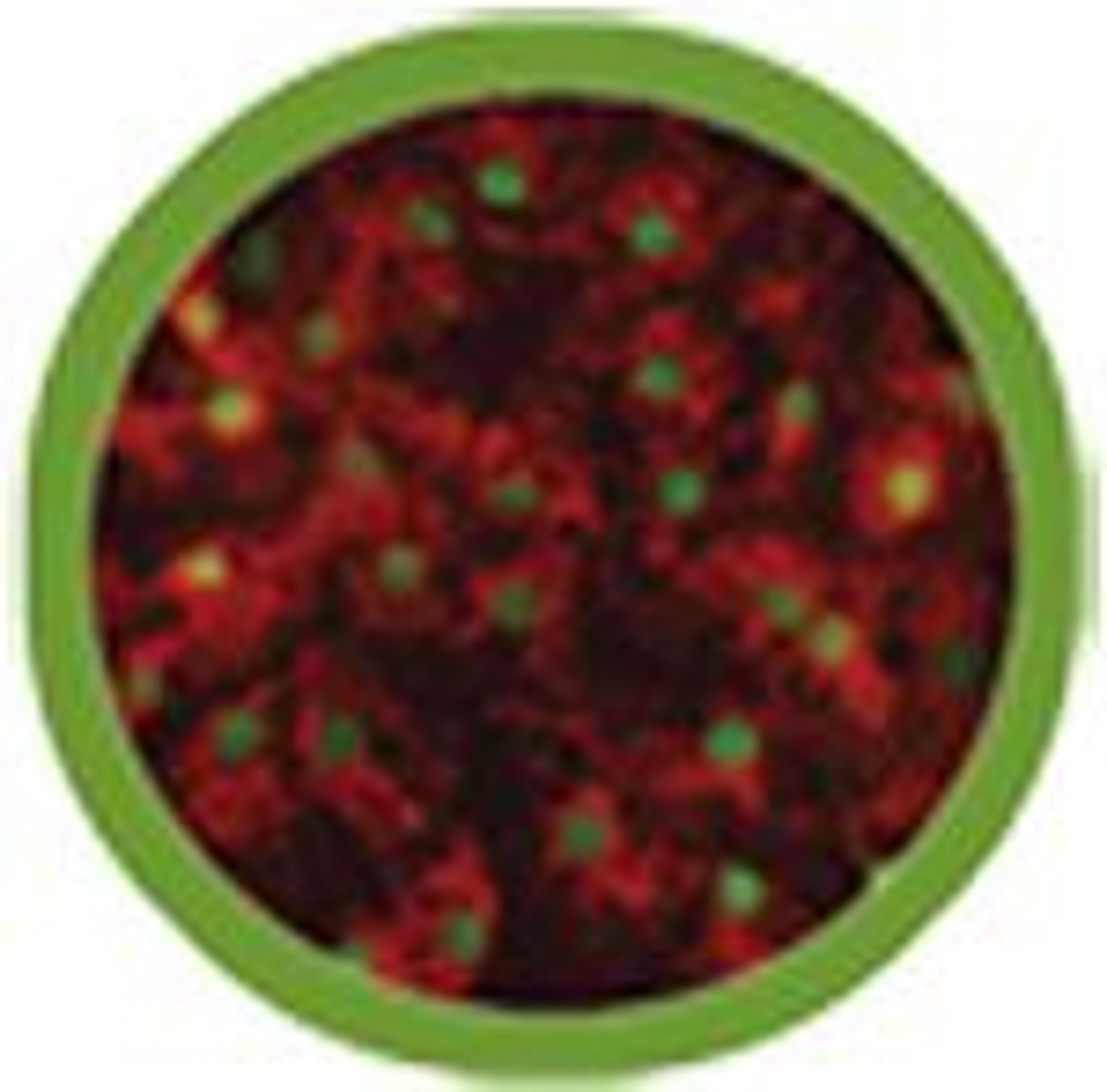
iCell® Hepatocytes, derived from human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, provide access to commercial quantities of high quality, high purity human liver cells for preclinical drug discovery, hepatotoxicity testing, and disease research. iCell® Hepatocytes express alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT), asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGR1), hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4A), and secrete albumin at levels similar to adult primary…

The supplier does not provide quotations for this product through SelectScience. You can search for similar products in our Product Directory.
iCell® Hepatocytes, derived from human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, provide access to commercial quantities of high quality, high purity human liver cells for preclinical drug discovery, hepatotoxicity testing, and disease research.
iCell® Hepatocytes express alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT), asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGR1), hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4A), and secrete albumin at levels similar to adult primary human hepatocytes. In addition, the cells exhibit intrinsic metabolism (e.g. glycogen and lipid storage), xenobiotic metabolism, and transporter functions. Importantly, iCell Hepatocytes respond appropriately to known hepatotoxicants and support HCV and HBV infection.
iCell® Hepatocytes are currently shipped as fresh cells, which remain viable and functional for at least 3 weeks following plating on collagen-coated plates. Thus, these cells can be used for acute and longer-term assays for targeted drug discovery, toxicity testing, and other life science research.
iCell® Hepatocytes Benefits:
- Human Cells - Hepatocytes are terminally differentiated from human iPS cells and exhibit hepatocyte characteristics and functions.
- Homogenous and Reproducible
- Functionally Stable
- Known Genotype - Hepatocytes have been genotyped for 1,936 ADME markers in over 200 genes, including all FDA-validated genes and >90% of the ADME Core markers as defined by the PharmaADME group.
iCell® Hepatocytes Applications:
- Heptatocytes are amenable to a variety of biochemical and cellular assays: Hepatoxicity, Intrinsic metabolism, Xenobiotic metabolism, Transporter function, Viral infectivity.