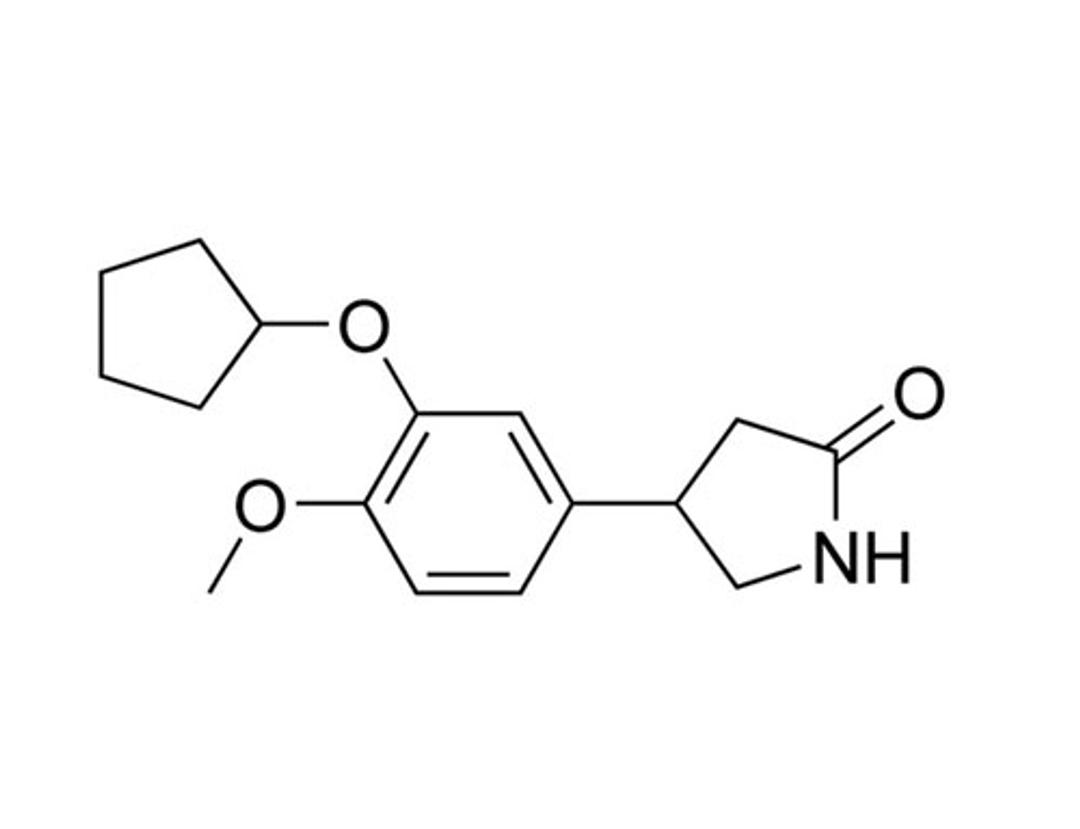
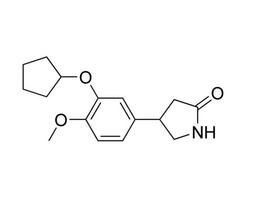
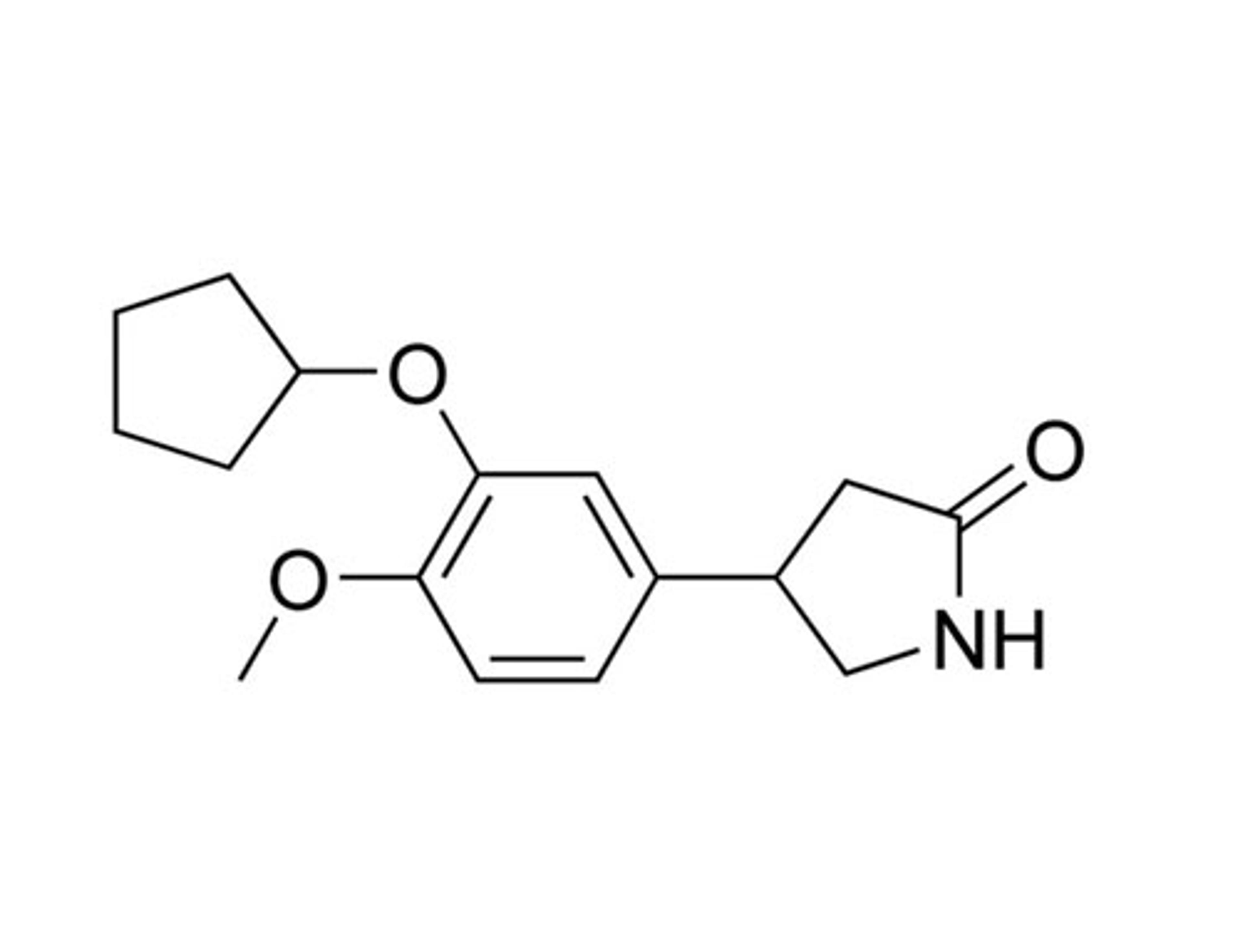
Rolipram
cAMP pathway activator; Inhibits type 4 cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDE4)

The supplier does not provide quotations for this product through SelectScience. You can search for similar products in our Product Directory.
Rolipram is a cell-permeable, selective inhibitor of Type 4 cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDE4), which mediate cyclic AMP (cAMP) degradation. Rolipram preferably inhibits PDE4 isoform A (IC₅₀ = 3 nM) over other isoforms such as B and D (IC₅₀ = 130 and 240 nM respectively; MacKenzie & Houslay). It inhibits interferon (IFN)-γ stimulated phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase through PDE4B and/or PDE4D isoform inhibition (MacKenzie & Houslay).
DIFFERENTIATION
- Enhances osteoblastic differentiation of mouse mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) induced by BMP-2 (Munisso et al.)
- Induces neural differentiation of human bone marrow-derived MSCs (Alexanian et al.)
REPROGRAMMING
- Induces reprogramming of adult human dermal fibroblasts (AHDFs) into induced neuronal stem cells, in combination with A83-01, CHIR99021, sodium butyrate, LPA, SP600125, and exogenous OCT4 expression (Zhu et al.)
DISEASE MODELING
- Promotes survival of newly formed mouse hippocampal neurons in a mouse model of ischemia (Sasaki et al.)
- Reverses amphetamine-induced reductions in auditory-evoked potentials in a C57BL/6J mouse model of schizophrenia (Maxwell et al.)
IMMUNOLOGY
- Inhibits inflammation by suppressing leukocyte function, inhibiting C5a-stimulated leukotriene C4 (LTC4) synthesis in human eosinophils (Tenor et al.)
- Inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced tumor necrosis factor (TNF) synthesis in human monocytes (Souness et al.)